What are Concussions?
Concussions are caused by force to the head causing a change in head motion and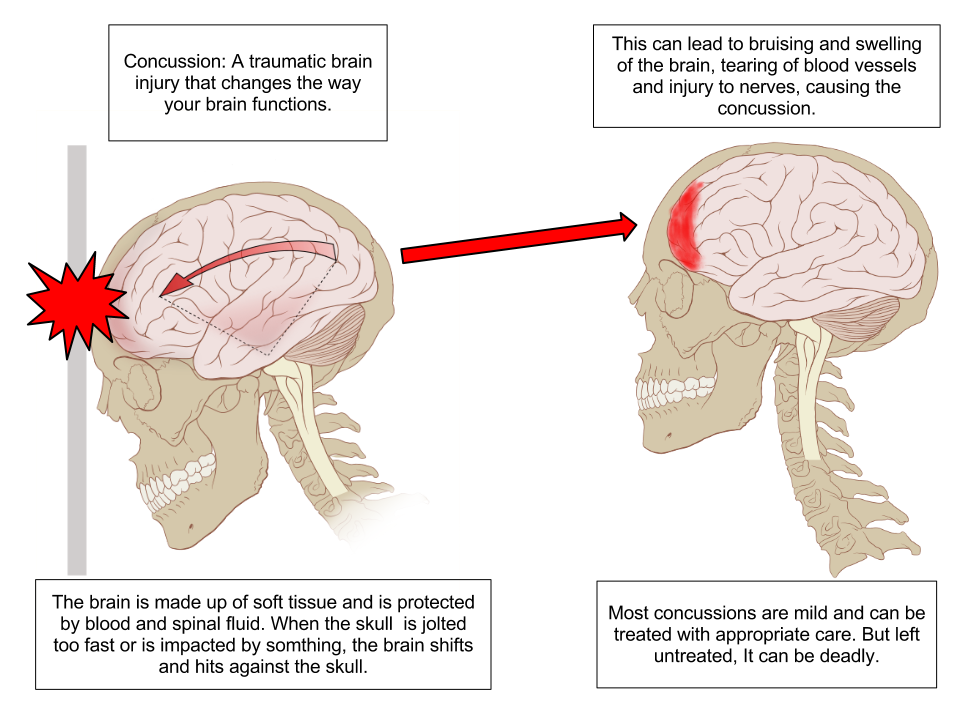 possible skull deformation. Depending on the force, position and angle of contact,concussions can vary in severity and symptoms. Typical symptoms stem from a cascade of molecular events inside the brain that shift from normal function. Balances of major ions in the brain like potassium, glutamate, and calcium are shifted during concussions, requiring energy in the form of ATP to return to homeostasis. This in turn calls for an influx of glucose to provide the ATP to the
possible skull deformation. Depending on the force, position and angle of contact,concussions can vary in severity and symptoms. Typical symptoms stem from a cascade of molecular events inside the brain that shift from normal function. Balances of major ions in the brain like potassium, glutamate, and calcium are shifted during concussions, requiring energy in the form of ATP to return to homeostasis. This in turn calls for an influx of glucose to provide the ATP to the cell. After this initial influx in ATP and glucose, there is a depression of both compounds following concussion. The development of free radicals is also a result of concussion, causing damage to DNA and other fragile cell material. Other effects of concussion include damage to axons, synaptic plasticity, and connectivity changes.
cell. After this initial influx in ATP and glucose, there is a depression of both compounds following concussion. The development of free radicals is also a result of concussion, causing damage to DNA and other fragile cell material. Other effects of concussion include damage to axons, synaptic plasticity, and connectivity changes.
Diagnosing/Analyzing Concussions
Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Measures the structure of axons with measures of how much water diffuses (mean diffusivity) and what the directionality of diffusion is (FA).
Fractional Anisotropy: Measures how water particles diffuse in a particular environment like your brain. Diffusion of particles, and therefore FA value, is affected by many structural differences in the nerve fibers such as size, myelination, volume, density, and orientation. With all of these effectors, FA can be used to evaluate the content of a brain’s white matter, which coordinates communication throughout the brain. In concussions, typically a drop in FA values are seen as a long term effect, possibly due to a decrease in nerve fiber volume. Some cases show an increase in FA value right away, pointing to a possible neuro-inflammatory response.
Treatments for Concussion
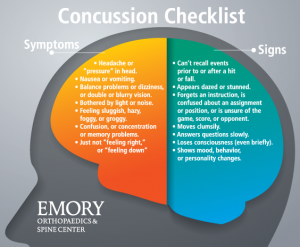 While there is no way to stop the cascade resulting from concussions, symptoms can be regulated with plenty of rest and reduced stimulation. Staying away from screens and intense reading can increase the recovery speed, and help alleviate symptoms like headache and difficulty focusing on things. Rest in this case means not doing things that exacerbate symptoms
While there is no way to stop the cascade resulting from concussions, symptoms can be regulated with plenty of rest and reduced stimulation. Staying away from screens and intense reading can increase the recovery speed, and help alleviate symptoms like headache and difficulty focusing on things. Rest in this case means not doing things that exacerbate symptoms
Further Research
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/concussion/symptoms-causes/syc-20355594
- http://advancingyourhealth.org/orthopedics/2015/12/30/key-steps-to-diagnosing-and-treating-concussions/
- http://www.protectthebrain.org/Brain-Injury-Research/What-is-a-Concussion-.aspx
Images
