What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a general term for several disorders that cause nervousness, fear, apprehension, and worrying. Anxiety plays a profound role in the impact of psychologically stressful events on physiological, behavioral, and cognitive responses. Stressful events can be anything, such as tests, recitals, or interviews. They are several types of anxiety that we will discuss later.
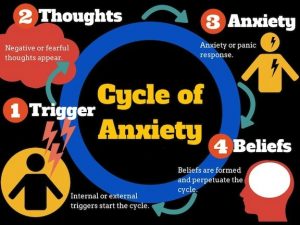
In the brain.
- Stress evokes activation of GABA receptors
- GABA (gamma-Aminobutyric acid) (learn more about Gaba here https://www.everydayhealth.com/gaba/guide/) decrease in the brain (hippocampus, dentate gyrus)
- Decreased GABA Leads to an increase in histone H3 which makes memories stronger.
- We don’t want to make stronger memories of stressful events. Which is what happens in people with anxiety.

What causes anxiety?
As we have seen above, abnormality in the brain can lead to anxiety. Other factors such as the environment, substance use and abuse and medical can also induce anxiety.
- Environmental factors
- Stress from work, school, financial difficulties, natural disaster, etc
- Trauma from events such as abuse, victimization, or the death of a loved one
- Medical factors
- Lack of oxygen from emphysema, or pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lung)
- Stress from a serious medical illness
- Side effects from medication
- substance use and abuse
- certain studies have indicated that the increase use of alcohol and drugs play a role in influencing anxiety within users. https://search.proquest.com/openview/b61ecfe6889e591d0e957c25840480e5/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=40661
Types of anxiety
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- chronic disorder
- long-lasting anxiety
- Excessive worry about money, health, work, school.
- have trouble identifying specific fear
- Most common form of anxiety.
- Panic Disorders
- Characterized by brief or sudden attacks intense terror
- Shortness in breath, dizziness, confusion and other attacks may occur
- Attacks can last for hours
- They can be spontaneous but usually occurs after scary and frightening experiences
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- fear of being negatively judged by others or a fear of public embarrassment due to impulsive actions
- affects 5% of the general population
- failure to interact with the environment around which leads to avoidance of the environment
Other form of anxiety include, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Phobias, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), and Separation Anxiety Disorder.
Treatment for anxiety.
Anxiety can be treated by medication, counseling and self-treatment. Medication is preferred as the last resort for people with anxiety due to its ability to present side effect.
- Learning to reduce stress by being mindful of stressful environment and other self-awareness practices such as, deep breathing, self-talk and exercise have been shown to reduce levels of anxiety.
- Counseling methods like Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) which aims to recognize and change the patient’s thinking patterns that are associated with the anxiety and troublesome feelings, have also be productive in reducing anxiety
- Anxiety medication include Lorazepam (Ativan), Diazepam (Valium), Clonazepam (Klonopin) and Alprazolam (Xanax)
Note: Sometimes alcoholism, depression, or other coexisting conditions have such a strong effect on the individual that treating the anxiety disorder must wait until the coexisting conditions are brought under control.
