 Let’s be honest, the most information the general population receives regarding schizophrenia comes from movies, TV shows, and other forms of media. While these can be very entertaining, they do not often show the true story behind schizophrenia and how it can affect someone’s daily life. So let’s break it down: we will get a quick overview of what schizophrenia is before discovering what is causing schizophrenia in the brain and what it means to live with schizophrenia.
Let’s be honest, the most information the general population receives regarding schizophrenia comes from movies, TV shows, and other forms of media. While these can be very entertaining, they do not often show the true story behind schizophrenia and how it can affect someone’s daily life. So let’s break it down: we will get a quick overview of what schizophrenia is before discovering what is causing schizophrenia in the brain and what it means to live with schizophrenia.
First of all, schizophrenia is a chronic psychiatric disorder that is one of the leading causes of disability in the world. The psychiatric symptoms commonly associated with schizophrenia are hallucinations and delusions. These symptoms make it especially difficult for schizophrenics to go about their daily lives, as reality is altered. Symptoms can also include speech impairments, lack of emotion, amnesia, and compulsiveness.
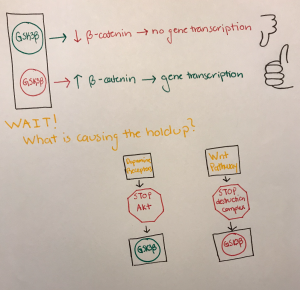
In the brain, GSK3B (glycogen synthase kinase 3 B) is a main component of something called an intracellular destruction complex. When it exists, this complex reduces the levels of B-catenin in your cells. B-catenin is a protein that is largely involved in the transcription of genes and without it, certain genes that are important for the processes involved in learning, responding, interacting, and memory are not transcribed. This is what occurs in schizophrenia, GSK3B is overactive and important genes are not transcribed. GSK3B levels increase when there is an increase in dopamine receptor activation because dopamine receptors turn off an enzyme called Akt, which is important for the inactivation of GSK3B. Without the activation of Akt, GSK3B is under no restraints and is able to destroy B-catenin.
The activity of GSK3B is typically kept in check by the Wnt signaling pathway. This pathway, when activated, destroys the destruction complex, thus rendering GSK3B inactive. This allows an increase in B-catenin that will then enter the nucleus of a cell and cause transcription of genes. In schizophrenia cases, the Wnt pathway is not destroying the destruction complex, allowing GSK3B to reduce levels of B-catenin.
Living with schizophrenia means being on a lifelong treatment plan. Antipsychotics are prescribed for schizophrenics. These drugs often target the GSK3B pathway described earlier by blocking the dopamine receptors. Physicians may also prescribe anti-depressants and anti-anxiety medications to help with the symptoms.
Schizophrenia is a complex disease and there is still a lot left to learn about the pathways and proteins involved. It is important to try to understand what is going on in the brain of an individual with a psychiatric disorder so the actions of the individual are understood and can be taken care of in a healthy way.