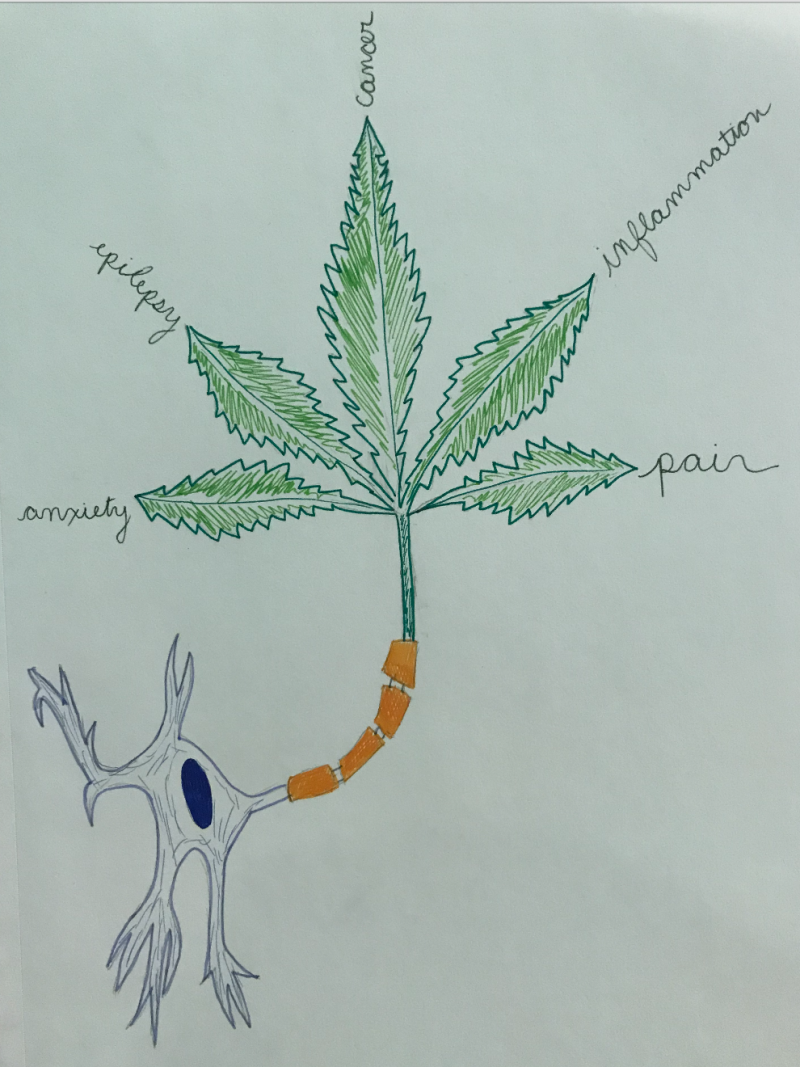
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is widely distributed throughout the body, with various receptors and actions. For these reasons, the ECS is very important for many physiological processes. Due to the variety of roles the ECS can play, it has become a target for pharmacological systems. But, as with the development of any treatment, there are some questions as to whether targeting the ECS with cannabis is the best course of action. This is due to nature of THC, a component of cannabis, which induces unwanted effects because of its psychotropic effects and potential for abuse.
Cancer
Cancer occurs when cells multiply too fast, causing abnormal cell growth and the potential to invade other parts of the body. CB1 receptors are more abundant in cancerous cells, so they bind cannabinoids more often. Cannabinoids have been known to induce apoptosis, or cell death. So if cannabinoids are released and bind to the abundance of CB1 receptors in cancer cells, the cancer cells will die and metastasis of the cancer will have been prevented.
Pain
Cannabinoids reduce pain through the activation of TRPV receptor. A TRPV receptor is one of the receptors in the ECS and is involved in the transmission and modulation of pain. Treating pain with cannabinoids works through desensitization. As cannabinoids bind to CB1 receptors (other ECS receptors), the receptors become desensitized and build up a tolerance. As these receptors become down regulated, their agonists, substances that initiate a response, bind TRPV1 and decrease activity. After repeated exposure, TRPV1 receptors can also become desensitized. The desensitization of TRPV1 receptors means there will be less pain transduction.
Migraine
During a migraine, patients often have sensitivity to light and sound. This is due to hyperactivity of neurons in their brain. Endocannabinoids can help with this symptom because they inhibit glutamatergic neurons, the neurons that have an increase in firing. Migraines are also a result of inflammation in the brain. There is also vasodilation in the dura of the brain that induces an immune response, causing inflammation in the brain. The inflammation is due to an inflammatory protein called calcitonin gene related peptide, which is associated with migraines. Nitric oxide induces vasodilation and since cannabinoids inhibit nitric oxide, this is one way they can treat migraines.

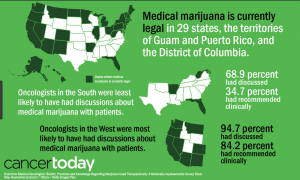
Cannabis has also been researched as a treatment for anxiety, Parkinson’s, depression, epilepsy and more. The problems facing the use of cannabis as a treatment are due to the lack of research on the ECS. It is very difficult for labs to obtain cannabis to use in research, as it is highly regulated by the FDA. Without adequate research, it is difficult to know how many different systems in the body are being affected by a dosage of cannabis. Using the endocannabinoid system as a treatment for many different health concerns is very promising. Before any decisions can be made, more needs to be understood in regards to the many varying physiologic pathways activated by cannabinoids.