The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system consists of three parts:
- Endocannabinoids
- Enzymes that synthesize and break down endocannabinoids
- Receptors that bind endocannabinoids
There are two endocannabinoids that are most prevalent to the system, anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). These molecules are cleaved from bigger lipids that are a part of cell membranes until being released to form endocannabinoids. This “on demand” synthesis is done by enzymes that cleave sections of the lipids that go on to signal through the endocannabinoid receptors. The synthesis only takes place when there is an increase in calcium in the cell, membrane depolarization, or receptor activation. With that, endocannabinoid signaling is highly regulated and stabilizes signaling throughout the body.
endocannabinoids. This “on demand” synthesis is done by enzymes that cleave sections of the lipids that go on to signal through the endocannabinoid receptors. The synthesis only takes place when there is an increase in calcium in the cell, membrane depolarization, or receptor activation. With that, endocannabinoid signaling is highly regulated and stabilizes signaling throughout the body.
Video: Endocannabinoid signaling and the components of the endocannabinoid system
There are two types of receptors most often used in the endocannabinoid system, CB1 and CB2. Both are G-protein coupled receptors that inhibit cyclic-AMP. CB1 receptors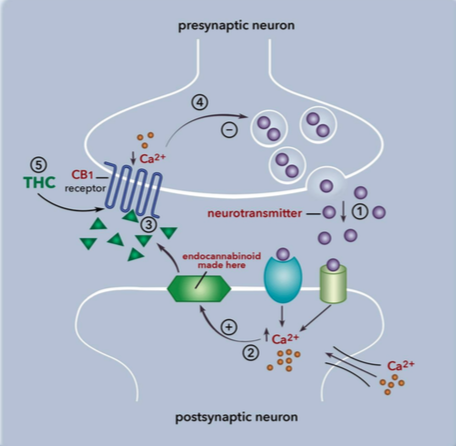 are most often found in the brain and nervous tissue, while CB2 are found in immune tissues. Inhibition of cyclic-AMP leads to a decrease in excitability and signaling, preventing action potentials from spreading between neurons. The endocannabinoid system is a component in many diseases, and can be targeted for many therapeutic benefits. One of these benefits is reducing the signaling associated with pain.
are most often found in the brain and nervous tissue, while CB2 are found in immune tissues. Inhibition of cyclic-AMP leads to a decrease in excitability and signaling, preventing action potentials from spreading between neurons. The endocannabinoid system is a component in many diseases, and can be targeted for many therapeutic benefits. One of these benefits is reducing the signaling associated with pain.
Pain and the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system can be us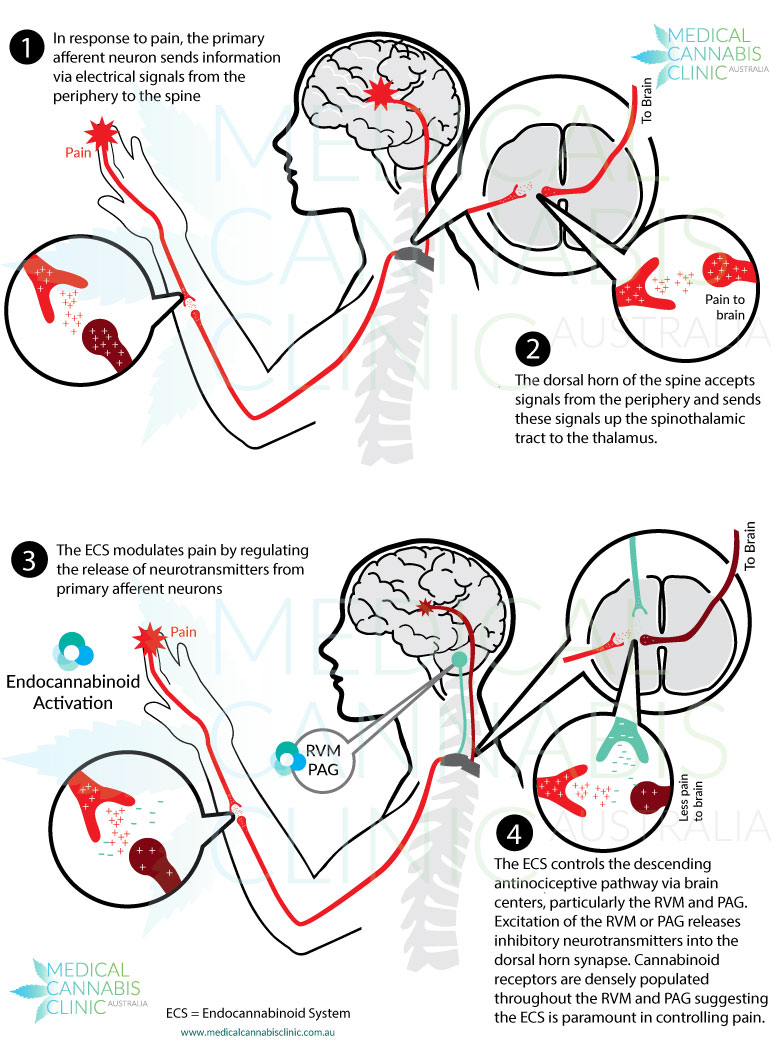 ed to target the pain nociception pathway. Endocannabinoids function to inhibit signaling that uses the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate by inhibiting cyclic-AMP. In CB1 receptors, this inhibition extends to the pain pathway, and can inhibit signaling in areas of the brain like the amygdala, periaqueductal grey matter, rostral ventromedial medulla, and superficial dorsal horn. CB2 receptors can also play a role in anti-pain signaling, as they are expressed in several cells with inflammatory and immune-competent nature. The inhibition of these cells therefore causes relief from pain caused by inflammation.
ed to target the pain nociception pathway. Endocannabinoids function to inhibit signaling that uses the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate by inhibiting cyclic-AMP. In CB1 receptors, this inhibition extends to the pain pathway, and can inhibit signaling in areas of the brain like the amygdala, periaqueductal grey matter, rostral ventromedial medulla, and superficial dorsal horn. CB2 receptors can also play a role in anti-pain signaling, as they are expressed in several cells with inflammatory and immune-competent nature. The inhibition of these cells therefore causes relief from pain caused by inflammation.
References:
- https://www.cbdschool.com/the-endocannabinoid-system-explained
- https://metacangroup.com/endocannabinoid-system
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4120766/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01671.x
- http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/FamilyIntroductionForward?familyId=13
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2834283/#!po=9.77011
- http://jaoa.org/article.aspx?articleid=2093607
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jznQfMj9RWM
- http://communitybasedispensary.org/pain/x