
Development of Schizophrenia
There is no definite cause of schizophrenia. Most studies point to issues during pregnancy including genetics, abnormal brain development, infection during pregnancy, and complications during birth. Some studies suggest head injuries, stressful life events, and social isolation. https://www.steadyhealth.com/articles/schizophrenia-development Patients with schizophrenia show delays in milestones as children which suggests that development of schizophrenia develops much earlier than the timing of the onset of schizophrenic symptoms. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cge.12111
Current Drug Treatments
The most commonly used treatment is antipsychotic drugs that block dopamine receptors. There are issues with these medications however, they tend to present serious adverse side effects such as lightheadedness and blurred vision. They can also cause tardive dyskinesia, which is characterized by involuntary, repetitive movements. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schizophrenia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354449 Lithium is also used as a treatment for schizophrenia in conjunction with other drugs but is more commonly used for the treatment of bipolar disorder. It seems to work through the inhibition of GSK. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cge.12111
The Wnt Pathway
https://youtu.be/NGVP4J9jpgs This video gives a great overview of how the Wnt pathway works. The Wnt pathway has been implicated in schizophrenia. The antipsychotics mentioned earlier act on dopamine. The dopamine pathway ties into Wnt signaling through GSK3 which is decreased by the decrease of activation of dopamine receptors. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cge.12111
Lithium seems to work in a similar fashion. Lithium competes with magnesium and inhibits GSK3. There is also some evidence that lithium destabilizes the destruction complex mentioned in the video that exists when the Wnt pathway is off. This activates the Wnt pathway and helps to regulate some of the symptoms seen in both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cge.12111
The Role of Genetics
Schizophrenia is fairly rare in the general population, occurring in about 1% of people. However, it occurs in 10% of people who have a close family member with schizophrenia. This leads to the assumption that there are genetic factors at play. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/mutated-genes-schizophrenia-map-brain-networks Researchers have found that spontaneous mutations, that are not inherited from either parent play a role in schizophrenia development. Some of these mutations cause an increase in activity of GSK3 and a decrease in Wnt signaling. Mutations that are linked to schizophrenia all appear in the prefrontal cortex which is related to executive functioning in the brain.
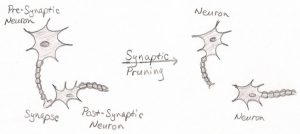
Other studies have found that there are mutations in deleted genes that are passed down from parents. Genetic mutations can cause unnecessary pruning of communications in the brains of teenagers who will later experience schizophrenic symptoms. Normally pruning in the brain is a good thing and gets rid of unnecessary connections within the brain as shown in the picture above. However, this goes wrong in schizophrenia. A gene known as C4 seems to be the culprit. C4 is responsible for tagging synapses for pruning, in schizophrenia it is overactive and causes too much pruning. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/schizophrenias-strongest-known-genetic-risk-deconstructed
Schizophrenia and Bipolar
Earlier I mentioned that GSK3 seems to be have an effect on both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. In schizophrenia elevated GSK3 affects brain development through deficits in the corpus callosum (connections between brain hemispheres) and connections to the thalamus which acts as the relay station for brain signals. There is evidence that in adults, elevated GSK3 interferes with microtubules which allow signals to be transmitted through the brain. https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(07)00035-5
Bipolar disorder also has an increase in GSK3 activity. The difference is what it does in the brain. The evidence suggests that the main action of GSK3 in bipolar disorder is apoptosis activity (cell death). This leads to smaller brain volume and the loss of neurons in areas of the brain that are related to the regulation of emotions. This relates to the extreme manic and depressive symptoms and quick switches between the two seen in bipolar disorder. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149763407000243
Conclusion
An increase in GSK3 and decrease in Wnt signaling presents a new target for the treatment of both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. The regulation of the Wnt pathway could allow for a treatment without the adverse effects of antipsychotic treatments. Genetic factors play a role in the development of schizophrenia that have not been fully discovered but some seem to directly affect Wnt signaling.
 bly.com/
bly.com/