The Endocannabinoid System
When a person speaks of cannabinoids, most people’s minds will automatically think of weed or CBD oil, but it is extremely important for people to understand that our bodies naturally create cannabinoids. More specifically, the body uses these
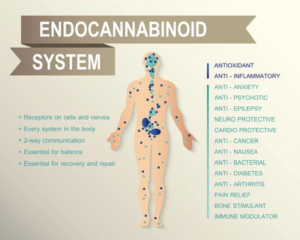
endogenous cannabinoids in the endocannabinoid system (eCS). The eCS play important roles in regulating other systems and responses such immune responses, communication between cells, appetite, metabolism, memory, and even more. Since the eCS regulates so many physiological aspects, problems can arise when when the system gets disrupted, and one physiological dysfunction that dysregulates the eCS affecting millions of people around the world is that of stress and anxiety.
Treating anxiety now
Short-term anxiety or stress may help a person respond to danger or get a task done right before the due date, but long term stress and anxiety can have negative effects on a persons health including gastrointestinal issues, heart issues, headaches, migraines, sleeping problems, or depression. To treat anxiety caused symptoms, doctors prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants), benzodiazepines, or beta-blockers. Although these medications may help suppress anxiety and its effects, they all cause various side effects including drowsiness, memory problems, insomnia, stomach problems or pains, and quite a few others. Considering the high amount of negative side effects given by anti anxiety medications, it is becoming increasingly more popular for scientists and pharmaceutical companies to look into other possible anti anxiety treatments. An new, exciting approach involves medications that regulate the endocannabinoid system to treat anxiety.
Relating anxiety and the eCS
When functioning properly, the endocannabinoid system helps to regulate the release of glutamate (the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the
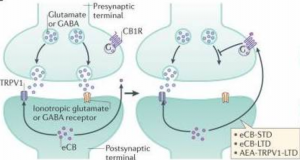
brain) and GABA (the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain). It inhibits the release of the neurotransmitters making it so they are not being released at too high of rates. It does this using the postsynaptic production of the endocannabinoids AEA and 2-AG. The endocannabinoids are released back into the synaptic cleft and the CB1 receptor reuptakes them which inhibits the release of glutamate and GABA. But, when the body is responding to stress and anxiety, there is an over production of FAAH and PTP1B which are enzymes that can breakdown endocannabinoids. In this scenario, the endocannabinoids are not being released to the synaptic cleft
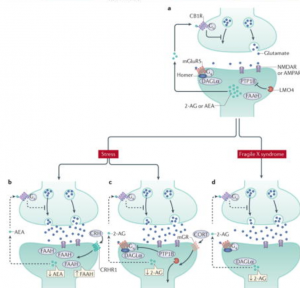
and therefore not activating the CB1 receptor. This allows for uncontrolled release of glutamate or GABA which can increase symptoms related to stress and anxiety. Since the eCS and anxiety are so closely related, introducing pharmaceutical forms of cannabinoids could be a potential treatment for anxiety.
Possible applications
Recently, there has been clinical trials that have shown promising treatments for anxiety using pharmaceuticals that affect the eCS. In the trials that have introduced drugs that have inhibited the breakdown of AEA by FAAH. There has also been promising research with using CB1 receptor agonists in helping with anxiety symptoms. Most likely, these medications could potentially be used in conjunction with currents anti anxiety medications or used as a starting treatment to treat acute anxiety disorders. Although the application of these medications affecting the eCS may be years away from being prescribed to patients, this is a promising and exciting science that may help to rid people with anxiety of the common symptoms caused by current anti anxiety medications.
