What is addiction?
Addiction is the compulsive seeking of an addictive substance or act despite horrible consequences. In addiction there is a loss of control, the individual can no longer determine their actions. The addiction I will be focusing on is drug addiction. Drugs have the ability to change the brain in a way that drives uncontrollable behaviors to seek out drugs and continue their consumption.
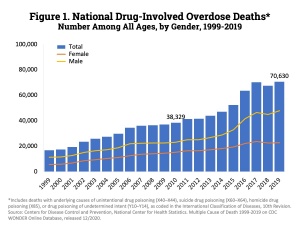
Since 2000, there have been over 700,000 deaths due to drug overdose in the US. 11.7% of Americans aged 12+ have used illegal drugs within the past 30 days. 165 million Americans aged 12+ currently abuse drugs, including alcohol, tobacco, and illegal drugs. Over 70,000 drug overdose deaths occur in the US annually. The number of overdose deaths increases at an annual rate of 4.0%. Figure 1, shows how many overdose deaths have occurred pere year since 1999.
9.5 million adults over the age of 18 have both a substance abuse disorder and a mental illness. There are more frightening statistics like these that could take up the rest of this post, but I think I have made my point. Drugs are scary and they cause disaster. 1
Drugs and your brain
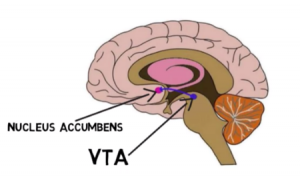
The circuit of the brain that receives the most attention in addiction is called the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway (ML-DA). In figure 2, you can see where in the brain this pathway is by the purple area between the two structures. This path is also known as the reward system. The start of the path is in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) a group of neurons located in the midbrain. 65% of these neurons are dopaminergic, meaning they produce the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine is our feel-good neurotransmitter, it doesn’t cause pleasure itself, but it induces other things to produce those feelings. When the VTA is activated by a stimulus it sends dopamine to the nucleus accumbens (NAc).
What kind of stimulus can activate the VTA?
There are three main stimuli that stimulate the VTA: a reward, anticipation of a reward, and a stressor. The type of stimuli will determine the kind of signal VTA neurons send and thus how much dopamine is produced. If the stimulus is a drug of abuse, the signal will send a lot of dopamine to the NAc.
The NAc is a region in the basal forebrain, and it is best known for its role in reward, cognition, reinforcement, and motivational salience. When this structure is stimulated by the dopamine from the VTA, it encodes a value to the stimulus. Researchers believe that the NAc is involved in stimulating actions to pursue rewards and inhibiting actions not helpful in obtaining a reward. The transitions between the two types of firing patterns form the VTA are thought to change concentrations of DA at the terminal and ultimately help encode the salience of stimuli, promote seeking of reward, and tune reward predication error for cue-associated behaviors.
There are some general assumptions provided for what dopamine does in this system. Dopamine is released in response to positive rewarding stimuli, but also in aversive stimuli & stress AND in the anticipation of a potential reward. This response to DA, is one of the reasons for the affective neuroethological perspective that views the ML-DA system in terms of its ability to activate an instinctual emotional appetitive state (seeking) evolved to induce organisms to search for all varieties of life-supporting stimuli and to avoid harms. This view is that the reward system not only aims to seek out rewards but also to avoid non-rewarding stimuli. Therefore, this could relate to the withdrawal factor of addiction. Symptoms of withdrawal are uncomfortable; thus, the reward system could stimulate the addict to seek out a reward (drugs). The memory of the NAc is that this drug has value, and this mechanism could potentially encode a value for a drug that is the same as food and water (actual life-sustaining substances).
Addiction is not a choice
After reading this information on how drugs change brain chemistry, you should understand that addiction is not a choice. Drugs create a hold on an individual that they cannot shake. Their brain has turned on them to need this drug for survival. Therefore, drug addiction is not easy to overcome. Drug addicts require our empathy for the disease state they are in. It takes tremendous strength to quit drugs of abuse, you can’t just stop taking drugs. Drugs are scary and they cause disaster.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3898681/