What does insulin do
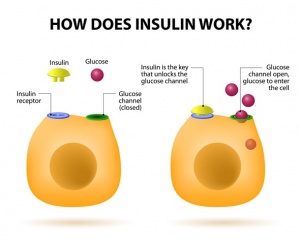
Insulin is a key regulator of adipose tissue lipolysis, which is the catabolic process leading to the breakdown of triglycerides stored in fat cells and release of fatty acids and glycerol (Langin et al., 2006). Insulin regulates adipose tissue metabolism through direct effects on adipocytes (a cell specific for storing fat) and through signaling in the central nervous system by dampening sympathetic outflow to the adipose tissue (Shin et al., 2017). So, what about insulin in relation to POMC and AgRP?
Regulating Hunger
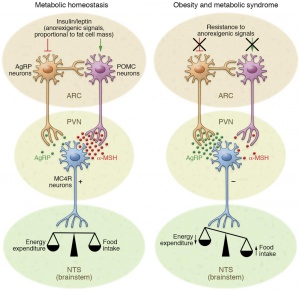
The insulin receptor is expressed in both AgRP and POMC neurons. Insulin can both inhibit AgRP and POMC through hyperpolarization or can activate these neurons as a result of heterogeneity (Shin et al., 2017). Insulin and leptin act directly on neuronal subsets in the ARC of the hypothalamus to control energy homeostasis. POMC neurons are activated, while AgRP neurons are inhibited. Then the MC4R-expressing neurons in the PVN. If one is fasting, the AgRP levels are increased and the POMC levels are reduced which leads to decreased MC4R signaling. When one has eaten, AgRP levels are diminished and POMC levels increase, which triggers MC4R signaling, stimulating energy expenditure (Jais et al., 2017).
Insulin resistance in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes is classified by decreased insulin-stimulated glucose transport and metabolism in adipocytes and skeletal muscle and by impaired suppression of hepatic glucose output. In this situation, insulin binding, receptor phosphorylation, and phosphorylation of IRSs are reduced. In general, this means that PI3K activity associated with both IRSs is impaired (Langin et al 2000).
Why is this Important?
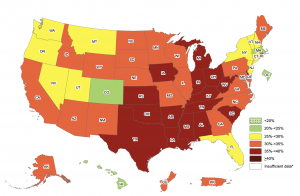
According to the CDC, the US obesity prevalence was 42.4% in 2017-2018. Obesity can lead to other disorders including, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer. These are among the leading causes of preventable, premature death (CDC et al., 2021).
What can I do to prevent this?
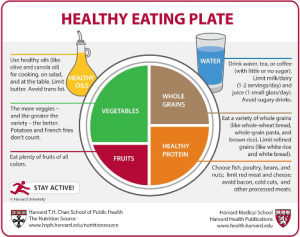
There isn’t necessarily a diet you can do to help prevent insulin resistance in your body, you must be willing to change your lifestyle all together. Obviously, everybody knows you should eat healthy, this isn’t new information, but it is important that when eating unhealthily it is in moderation. Although you should not skip meals because this causes your insulin and blood sugar levels to go up and down leading to more body fat (Moore et al., 2019). Try your best to adopt healthy habits slowly and they will become permanent.
Works Cited
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, September 30). Adult obesity facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved November 22, 2021, from https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html.
Jais, A., & Brüning, J. C. (2017). Hypothalamic inflammation in obesity and metabolic disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 127(1), 24–32. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88878
Kahn, B. B., & Flier, J. S. (2000). Obesity and insulin resistance. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 106(4), 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10842
Langin, D. (2006). Adipose tissue lipolysis as a metabolic pathway to define pharmacological strategies against obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Pharmacological Research, 53(6), 482–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2006.03.009
Moore, W. (n.d.). Insulin resistance diet: How to use Diet to prevent diabetes. WebMD. Retrieved September 23, 2019, from https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/diabetes-insulin-resistance-diet.
Shin, A. C., Filatova, N., Lindtner, C., Chi, T., Degann, S., Oberlin, D., & Buettner, C. (2017). Insulin receptor signaling in POMC, but not agrp, neurons controls adipose tissue insulin action. Diabetes, 66(6), 1560–1571. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-1238