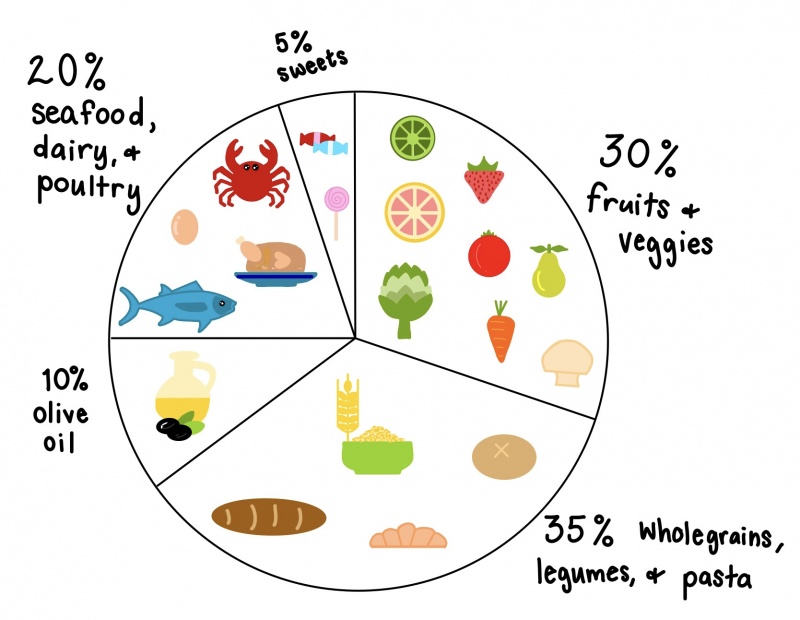
The ideal diet for humans contains high-quality food that is not processed such as veggies, fruits, whole grains, healthy fats, and protein. (1)
The ideal diet is the Mediterranean diet. This diet has been named the best 4 years in a row. It consists of mostly plant-based foods in addition to whole grains, seeds and nuts, spices and herbs, fruits and veggies, and olive oil. Fish, seafood, dairy, and poultry, are used sometimes while red meat and sweets are used rarely. Above is a hand-drawn diagram of the Mediterranean diet. (2)
Fatty fish and olive oil components of this diet are very healthy and have great benefits. Fatty fish can contain high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids which helps decrease inflammation, triglycerides, blood clotting, and risk of strokes and heart attacks. Olive oil is a monounsaturated fat that can lower cholesterol. The Mediterranea diet overall can decrease an individual’s chances of developing heart disease, stroke, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and type 2 diabetes. (2, 3, 4)
However, the Mediterranean diet can cause weight gain due to consuming higher amounts of fats from olive oil and nuts than what is recommended. A lower dose of iron from eating a small quantity of meat. Also, a decrease in calcium levels can be seen from consuming smaller portions of dairy products. (2)
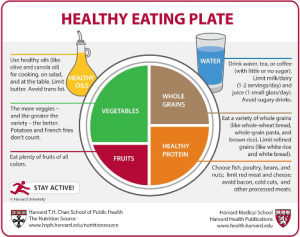
The new food guide consists of:
- 1/2 plate of diverse fruits and veggies
- 1/4 plate of whole grains (whole wheat, quinoa, brown rice, oats, etc)
- 1/4 plate of protein (fish, meat, etc.)
- Water, coffee, or tea (consume less dairy, juice, and sugary drinks)
History of the Ideal Diet
The ideal diet has changed throughout the years. There has been a total of 9 food guides for American citizens approved by the USDA.
The first guide was introduced in 1916 by Caroline Hunt called “Food for Young Children”. It aimed to guide parents and caregivers on proper nutrition for children. This guide included 5 groups consisting of:
- Cereals
- Fruits & veggies
- Meat & milk
- Fats & fatty acids
- Sugar & sugary foods

In 1917 Hunt and Helen Atwater created a food guide for the whole family called “How to Select Foods”. It included and guided parents and caregivers on ideal meals along with the estimated cost of each meal.

In 1943 the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) released the “Basic 7” food group guide to the public. This guide was made to help the United States citizens meet proper daily nutrition while rationing on food during World War II. Due to food rationing there the guide did not include serving sizes. The 7 food groups include:
- Green and yellow veggies
- Oranges, tomatoes, grapefruit, cabbage, and salad greens
- Potatoes and other fruits & veggies
- Milk and other dairy products
- Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dried beans, peas, nuts, and peanut butter
- Bread, flour, cereal, and natural whole grain
- Butter and fortified margarine

In 1955 the Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) introduced a shorted and condensed form of the “Basic 7” to the “Basic 4” which was approved by the USDA. This new guide included the food groups:
- Milk – includes the amount each age should consume daily
- Meat – 2+ servings per day
- Fruits & Veggies – 4+ servings per day
- Bread & Cereal – 4+ servings per day

In 1977 Mark Hegstend, a professor at HSPH developed the “1979 Hassle-Free Daily Food Guide”. This guide includes the food groups:
- Fruits & veggies – 4 servings
- Bread & cereal 4 servings
- Milk & cheese – 2 to 4 servings
- Meat, poultry, fish, & beans – 2 servings
- Fats, sweet, & alcohol – in moderation

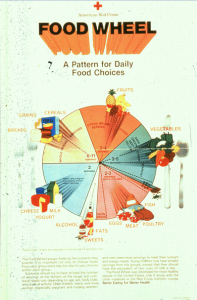
In 1984 the “Food Wheel” was developed and introduced by the American Red Cross and the USDA. This updated guide included the daily food groups and appropriate calorie intake. The groups included:
- Bread, grain, & cereal – 6 to 11 servings
- Fruits – 2 to 4 servings
- Veggies – 3 to 5 servings
- Eggs, meat, poultry, & fish – 2 to 3 servings
- Cheese, yogurt, & milk – 2 servings
- Alcohol, sweets, & fats – in moderation
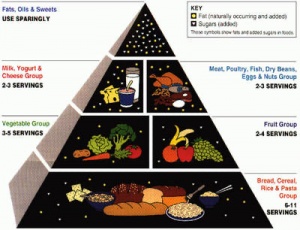
In 1992, the “Food Pyramid” was introduced. The large amount of recommended bread caused negative feedback of this guide. The 6 food groups included:
- Bread, cereal, rice, & pasta – 6 to 11 servings
- Fruits – 2 to 4 servings
- Veggies – 3 to 5 servings
- Milk, yogurt, & cheese – 2 to 3 servings
- Meat, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, & nuts – 2 to 3 servings
- Fats, oils, & sweets – in moderation
In 2005 “MyPyramid” was introduced. The graphic for the updated guide showed the importance of fitness along with adequate nutrition. The food groups include:
- Grains
- Veggies
- Fruits
- Milk
- Meat & Beans

In 2011 the USDA took a different approach to display food guides. “MyPlate” depicted the food portions on a plate rather than a pyramid, bullet points, or wheels.

This image was updated by HSPH to the “Healthy Eating Plate” and is held as the current food guide to American citizens. It stresses the importance of physical activity and eating healthy grains, proteins, oils, and vegetables that aren’t potatoes.

(5, 6)
Sources
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-weight/best-diet-quality-counts/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/mediterranean-diet/art-20047801
- https://www.helpguide.org/articles/diets/the-mediterranean-diet.htm
- https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2019/february/mediterranean-diet
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/magazine/centennial-food-guides-history/#jp-carousel-111354813228
- https://guides.lib.unc.edu/nutrition-history/government