The systems in the body are very well known in protecting it, with the immune system protecting against infection and the integumentary system protecting against debris. However, the endocannabinoid system is not a very well known system within the human body. This is a surprise as it has proven to have multiple helpful functions. It is described to play a key role during synaptic plasticity and homeostatic processes in the brain, making it a suitable spot for therapeutic treatments for disorders of the central nervous system [1]. It is involved in the use of Cannabis for your body as a therapeutic and treatment.
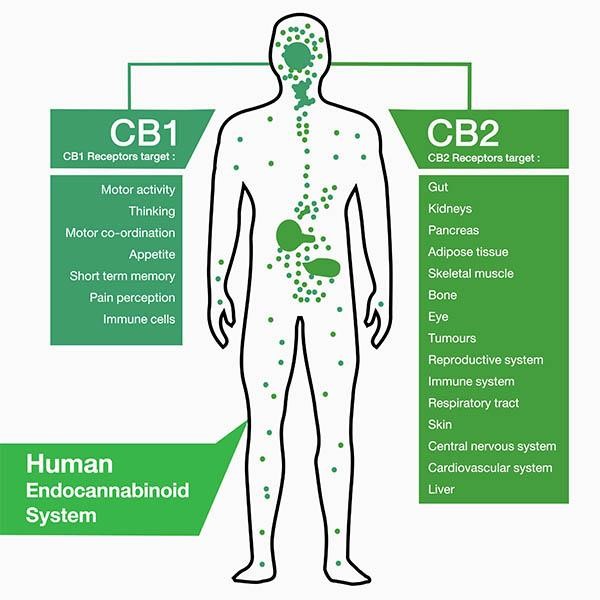
The endocannabinoid system is composed of two main receptors. The two main receptors of the endocannabinoid system are the CB-1 and CB-2 receptors, which determine the behavioral effects of the body when cannabis is consumed [2]. The CB-1 receptors are mainly located in the brain and other nerves throughout the body while the CB-2 receptors are mainly located in the immune and gastrointestinal systems [2]. The way these receptors work is that the CB1 is activated by arachnidonylethanolamine and 2-arachidnonylglycerol, coupling the CB-1 receptor to G proteins leading to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity leading to a decrease in levels of cAMP [1]. Locations and Targets for both receptors are shown on the diagram below.
The Cb1 receptors tend to bind to the central intoxicating component of cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol , making the Cb1 receptor play a major role in the euphoric effects of marijuana [3]. This means that when activating Cb1 receptors in your body this means that you have possibly smoked marijuana. Some of these symptoms that a person may experience in this situation includes the feeling of being on a high, pain relief, appetite, sedation and motor impairment, and cognitive and memory impairment [3].
The Cb2 receptors show another approach for brain disorder treatment by controlling synaptic functions involved in drug abuse and synaptic plasticity by inhibiting dopaminergic firing from the ventral tegmental area and reduced cocaine self-administration [1]. Based on the information gathered on both receptors, it is evident that the Cb1 receptor and Cb2 receptors are working around each other when exposed to cannabis.
While the endocannabinoid system has been linked to having roles in neurological diseases, there is some evidence of the receptors involved in treating people infected by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Hypotensive effects have been shown to be caused by activation of Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and mediation by ACE inhibition [4]. These effects have been linked to direct vasorelaxation effects that were induced by CB1 activation or ANG (II) vasoactive agonists [4]. Along with CB1 receptors, CB2 receptors are known to exert anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatine effects when stimulated [4]. This is present in the human lungs making it possible to use CB2 as a target for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections by reducing inflammatory responses.
This information shows that while the use of marijuana can have severe side effects on people who use it to the highest extent, there is a possibility that it can be used for treatment purposes through activation of the Cb1 and Cb2 receptors leading to the reduction of COVID-19 symptoms and infections. This is why it can be very useful to learn more on how the endocannabinoid system can have possible therapeutic and treatment effects on the person’s body.