What is Schizophrenia:
Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that is characterized by delusions and hallucinations. Delusions are false beliefs that an individual believes to be true. Delusions can be misinterpreting someone’s actions to be something more to the person with schizophrenia. Another symptom is hallucinations, hallucinations are where the individual experiences auditory and visual stimuli of something that does not exist. A majority of hallucinations are linked to hearing voices that are not present. Currently little is known about the cause of Schizophrenia and there are not any definite treatments.
Schizophrenia causes:
Numerous studies have looked at Schizophrenia to determine what causes and no clear-cut definite result has been determined. However, it has been observed that infection in utero has been linked to disrupting fetal brain development and contribute towards the child developing schizophrenia. A marker for schizophrenia at a young age is the delay of reaching cognitive milestones. Additionally, there has been a link between brain size and those diagnosed with Schizophrenia. Those diagnosed with schizophrenia have been observed to have less gray matter due to synaptic pruning and to have a smaller hippocampus and amygdala compared to an individual without schizophrenia.
Research has also looked at the genetics of schizophrenia and found that it is heritable. However, through exome sequencing it was discovered that a chromosomal mutation was responsible for the disease. A mutation on chromosome 14q32 reduces the production of the protein Akt. An imbalance of Akt has been linked to schizophrenia due to the protein’s role in the Wnt pathway.
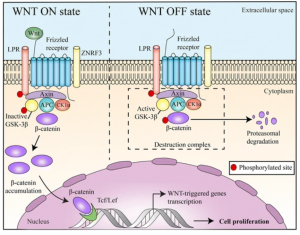
Wnt pathway:
The Wnt signaling pathway is responsible for neural circuitry development and synaptic plasticity. The Wnt pathway is activated by the binding of Wnt ligands to the frizzled receptor which results in the dissociation of the destruction complex and the decreased phosphorylation of β-catenin. This allows for the accumulation of β-catenin and for the translocation to the nucleus for gene transcription. However, in the absence of the Wnt ligand binding the Axin, APC, CK1α complex is destroyed. The destruction of this complex leads to the activation of GSK-3β and the proteasomal degradation of β-catenin. The consequence of this is that GSK-3β will continue to tag β-catenin for degradation not allowing it to continue to the nucleus. Without proceeding to the nucleus for gene transcription cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis are not able to be carried out.
Schizophrenia treatments
Schizophrenia is characterized by a reduction in β-catenin. Due to β-catenin being produced by the Wnt pathway dysfunction of the pathway is the leading cause of Schizophrenia. Therefore, activation of the Wnt signaling pathway is hypothesized to aid in the treatment of schizophrenia. One treatment method would be to inhibit dopamine signaling on the D2 receptor. Overabundance of dopamine has been recorded as a precursor to schizophrenia and directly activates GSK-3β, in turn degrading β-catenin. Therefore, by inhibiting dopamine Wnt signaling could be stabilized. Another potential treatment is Lithium, lithium directly inhibits GSK-3β since it competes with the binding of magnesium. Lastly, treatments that target metabotropic glutamate receptors could be a potential treatment. Targeting these receptors would increase Akt activation, decrease GSK-3β activation, ultimately resulting in β-catenin accumulation.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a life altering disorder that leaves individuals with numerous debilitating symptoms. However, with the help of current research a link between the Wnt signaling pathway and schizophrenia has been found. With this knowledge schizophrenia may be more effectively treated since the dysfunctional pathway is known. By knowing that reduced β-catenin levels due to the dysfunction of Wnt signaling are the culprit for schizophrenia drugs that target the activation of the Wnt pathway, inhibit D2 dopamine receptors, inhibit GSK-3β, or activate Akt are potential treatments for raising β-catenin levels and ultimately treating schizophrenia.
References
- Feature image: https://www.tpr.org/bioscience-medicine/2018-12-06/san-antonio-man-working-to-erase-stigma-of-schizophrenia
- Pathway schematic: https://jhoonline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13045-017-0471-6
