What is the endocannabinoid system?
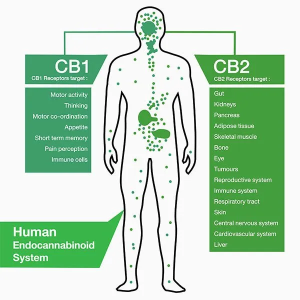
The endocannabinoid system is a neuromodulatory system that is important in the central nervous system for the role it plays in maintaining synaptic plasticity and homeostasis in the brain. This system controls mood, pain, perception, learning and memory, along with other things as well. It also has a neuroprotective role during traumatic brain injuries. An important part of the endocannabinoid system includes the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 along with a few others. The CB1 receptor has been connected to pathophysiological events ranging from memory deficits to neurodegenerative disorders. The CB1 receptor, therefore, is very important in maintaining well-being. But what is the CB1 receptor exactly that makes it so important for human health? It is one of the most commonly found G protein coupled receptors in the central nervous system, specifically in the neocortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and brainstem. A receptor found in such high quantities is bound to play a very impactful role in brain homeostasis. They specifically bind to cannabis sativa, more commonly known as marijuana and THC. On the other hand, CB2 receptors have a more defined pattern of expression and are primarily found in cells and tissues of the immune system. CB2 receptors are associated with inflammation and are localized to microglia.
Cannabis
THC and CBD (cannabidiol) are both cannabinoids that are derived from cannabis plants. While CBD does not produce the high sensation often associated with cannabis, THC absolutely does. THC is a cannabis that has over 60 ligands for CBs, so exposure to it can cause paradoxical effects in humans like relaxation, dysphoria, tolerance, and dependence. However, these effects are blocked with a selective blocker of CB1 receptors. This is because THC must bind with the CB1 receptors to produce a sense of euphoria. Furthermore, THC has positive effects on spasms and pain associated with MS. THC may show improvement in those with multiple sclerosis due to the link between CB1 and CB2 receptors and anti-inflammation effects in CNS. For other common medical purposes, THC has benefits to reduce pain, insomnia, low appetite, nausea, anxiety, etc. However, people might prefer CBD over THC because of the lack of side effects that can occur with THC. CBD has also been shown to help with conditions like seizures, inflammation, pain, mental disorders, migraines, depression, and anxiety.
A long history
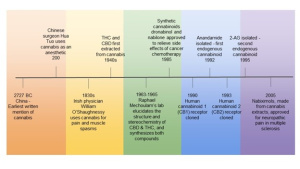
Cannabis has been around for quite a long time in different cultures across the world. Cannabis was officially attested to nearly 12,000 years ago near the Altai Mountains in Central Asia. South-East Asia has also been proposed as an alternative region for the primary domestication of cannabis where it was used for fibers for ropes and nets, food, and seeds for oil. However, as for medical purposes, the earliest records point to usage in China. The discovery of the curative
properties of these plants was said to be made by Shén Nóng, a mythical emperor whose name means the Divine Farmer in the 20th century BC. Later, Europe rediscovered the medicinal and psychoactive properties of cannabis through the translation of Arabic books and manuscripts followed by the scientific observations made by physicians of their time. Eventually, Western medicine became quite popular in the late 19th and early 20th century. During this popularization, Queen Victoria took cannabis for cramps, while Empress Elisabeth of Austria took it for cough and appetite stimulation. While it was used often in the past, it is sort of a taboo in our current American society. Today, telling a friend you took cannabis for cramps may raise some eyebrows. Nevertheless, it is still making a comeback for its medical purposes in the healthcare system today.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system, composed of two primary receptors CB1 and CB2, is important in brain homeostasis. Cannabis has been around for centuries and while research on it has not been done in depth, there is enough proof of the effects that it can have on human health and well-being. For years, cannabis has been medically used in different regions of the world. Today, it is making a medical use comeback, although it also has negative side effects that make people hesitant on relying on it for medicine.
Citations
- Kendall, D. A., & Yudowski, G. A. (2017). Cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system: Their signaling and roles in disease. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00294
- Hiding in plain sight: The discovery of the endocannabinoid system // International League Against Epilepsy. (n.d.). Retrieved May 2, 2023, from https://www.ilae.org/journals/epigraph/epigraph-vol-21-issue-1-winter-2019/hiding-in-plain-sight-the-discovery-of-the-endocannabinoid-system
- The endocannabinoid system: How cannabinoids take effect. (2019, November 15). https://www.encore-labs.com/the-endocannabinoid-system-how-cannabinoids-take-effect
- Holland, K. (2020, July 20). CBD vs. THC: What’s the difference? Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/health/cbd-vs-thc
- Crocq, M.-A. (2020). History of cannabis and the endocannabinoid system. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 22(3), 223–228. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.3/mcrocq
