A. The Pathway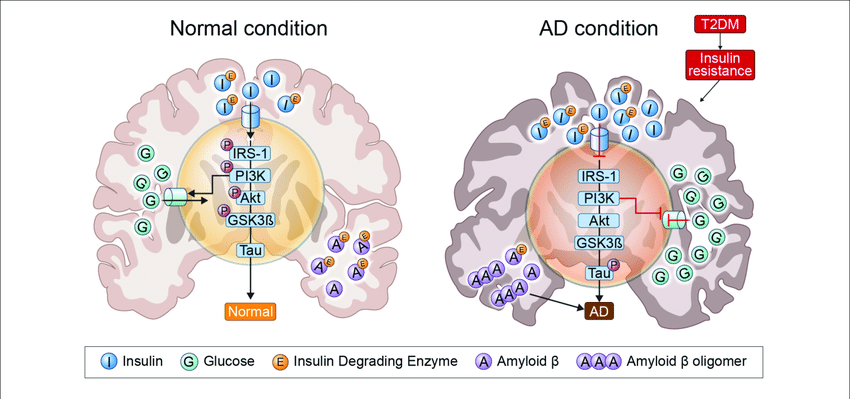
I/ Insulin in the body
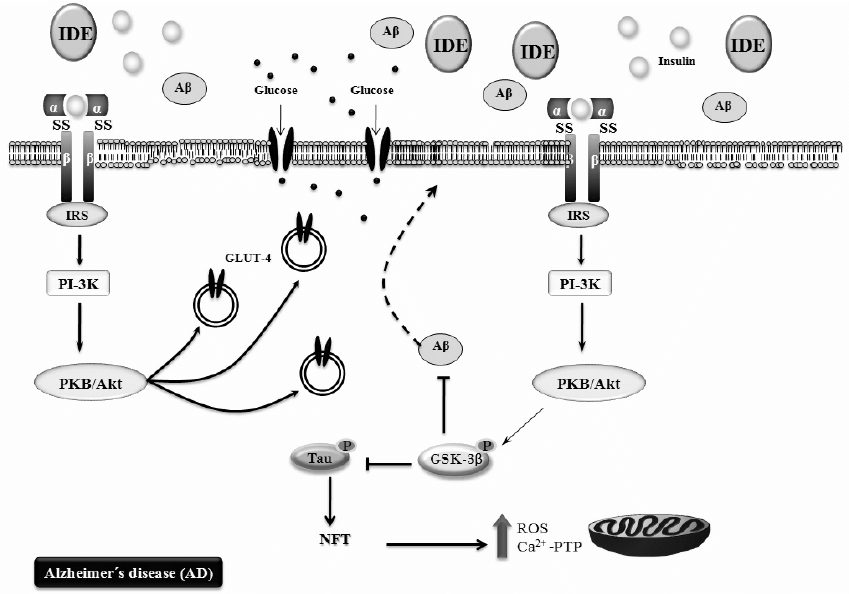
The insulin signaling pathway plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis in the body. Key molecules involved in this pathway include insulin receptor (IR), insulin receptor substrate (IRS), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt (protein kinase B), and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3).
In addition to its role in glucose metabolism, the insulin signaling pathway has been implicated in various cellular processes, including cell growth, proliferation, survival, and synaptic plasticity. Especially, in the brain, insulin signaling is particularly important for neuronal function and cognition, as insulin receptors in synaptic transmission and plasticity.
II/ Insulin and the brain
Recently, there is growing evidence suggesting that dysregulation of the insulin signaling pathway may contribute to neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For example, insulin resistance, characterized by impaired insulin signaling and reduced responsiveness to insulin, has been observed in the brains of individuals with AD. This insulin resistance may lead to dysfunction in glucose metabolism, energy deficits, oxidative stress, and impaired synaptic plasticity, all of which are implicated in the pathogenesis of AD.
Furthermore, abnormal activation of GSK-3, a downstream target of the insulin signaling pathway, has been linked to the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles, a hallmark pathological feature of AD. Inhibition of GSK-3 has been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy for AD.
B. Types and Treatments of AD
C. Future posibilities
Overall, the insulin signaling pathway plays a critical role in neuronal function and may represent a promising target for therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. While current treatments cannot halt or reverse the progression of AD, they can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with the condition. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms linking insulin signaling dysfunction to neurodegeneration and to develop effective therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway.
Bibliography
Akhtar A, Sah SP. Insulin signaling pathway and related molecules: Role in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int. 2020 May;135:104707. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104707. Epub 2020 Feb 21. PMID: 32092326.
http://https://www.researchgate.net/publication/38070626_Insulin_is_a_Two-Edged_Knife_on_the_Brain
http://https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353826555_Role_of_DPP-4_and_SGLT2_Inhibitors_Connected_to_Alzheimer_Disease_in_Type_2_Diabetes_Mellitus