When you think of a person who is a drug addict or an alcoholic, some people would think of typical stereotypes of them such as having no control over themselves. However, just because they are an addict doesn’t mean that they have no self control. Some people do not know all of what goes on in a person’s body when they become addicted to drug stimulants or sedatives. I believe it is important to understand the chemical and physical side effects while the drugs are in your system and when they are out of your system during a period of withdrawal.
One important piece of information about drug addiction is the changes in your body that can be caused by drugs. One such change is involved in epigenetics. Much of epigenetics is still unknown but it is defined as the changes or mutations on the outside structure of the DNA, specifically on the histones [1]. Histones are a group of proteins that the DNA wraps around to be condensed into chromatin and fit in the nucleus of a cell [2]. How much the DNA is condensed can be heavily influenced by the epigenetics of the histones. Two types of histone modifications are histone methylation, which causes the chromosomes to become more compressed and inhibit transcription, and histone acetylation, which causes the chromosomes to become loose and increase transcription [1]. More transcription means that the cell has more activity and more things that are being produced as opposed to no transcription with little activity in the cell. Drugs like cocaine and amphetamines can cause Histone acetylation because they act as stimulants [1]. This is but one change occurring on your body when you use drugs and it only gets worse the more you use them.
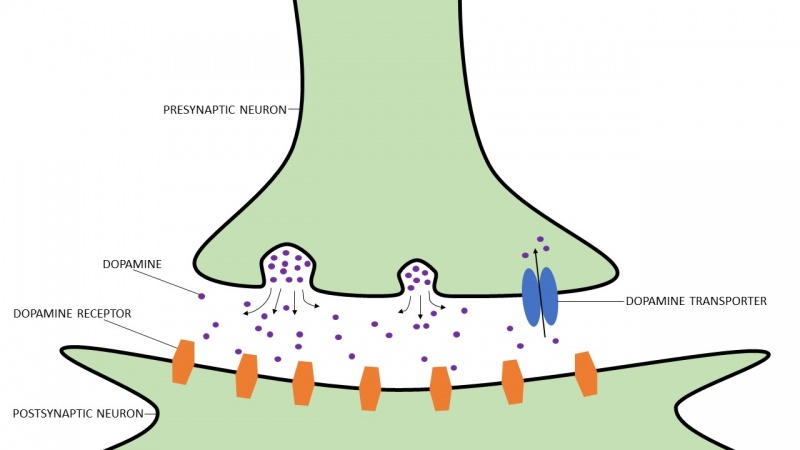
Another important change is involved in affecting synaptic plasticity of the person and this is probably the most detrimental change on the body. Synaptic plasticity is when there is a change in structure shown in the synapses between the neurons causing a type communication between them that results in an overall action. Different types of drugs can influence the synapses by hijacking and impairing their behavior and elicit the release of dopamine, a reward drug to make somebody feel good [1]. The mechanism of synaptic plasticity with the release of Dopamine is shown in the figure below. This explains why people do drugs because in a way, we all know how it feels. Whether we get a good grade on an exam or win a competition, dopamine is released so you feel a surge of pleasure and satisfaction that we would all like to experience. That is why people do drugs, to get the same feeling. However, the more you use the drug, the more your body gets tolerant of it so in order to get the same feeling of pleasure, you need to increase the amount you take, which can cause drastic effects on your body, especially if you want to try to stop [3].
With these changes caused by epigenetics and synaptic plasticity, it can cause a person to depend on the drugs to a degree that when they stop using drugs, they experience a great deal of withdrawal. Withdrawal can cause very harming physical and mental effects such as depression, fatigue, nausea, sweating, vomiting, restlessness, and sleep deprivation [4]. This shows that just because somebody is continuing to use drugs, despite knowing the side effects, doesn’t mean that they do not want to stop or that they just don’t have enough self control. It is possible that they keep using drugs because of the painful withdrawal effects they go through afterwards. It is because of these effects we should be more mindful and thoughtful of what drug addicts go through to stop and get clean.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3898681/
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/histones-57/
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/understanding-drug-use-addiction
- https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-withdrawal-how-long-does-it-last-63036