What is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder that is hallmarked by an individual’s abnormal interpretation of reality that interferes with their everyday lives. There are two categories of symptoms which are positive and negative symptoms. People with schizophrenia can display both types of symptoms at different times. The positive symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and disorganized behavior. The negative symptoms include things such as lethargy, lack of emotion, and general loss of interest in social activities.
Delusions: beliefs that are false and have no foundation in reality. Like if a person believes that they are the president of the United States.
Hallucinations: having a sensory experience without the presence of any actual stimulus. Like when you think you hear your name, but no one has said anything in the last five minutes.
Disorganized thinking patterns: this is marked by impaired speech patterns. Usually, people displaying this symptom may answer questions with words that aren’t relevant to the question, or they will string a bunch of random words together to make an incoherent sentence.
Disorganized behavior: this is marked by things such as strange posture and actions that have no clear goals, such as excessive movement.
Wnt Signaling Overview
Wnt signaling is a type of cell signaling that cells use to initiate gene transcription so they can make proteins. These proteins then are used for the normal functioning of the cell. The goal of Wnt signaling is to activate a chemical called B-catenin that is used to initiate gene transcription. Wnt is a signal that binds to a certain receptor in the cell membrane (called frizzled). Once frizzled is activated it recruits this complex of proteins called the destruction complex. Normally, this destruction complex is deactivating B-catenin, but when it is called away by frizzled than B-catenin is free to enter the nucleus and do its thing.
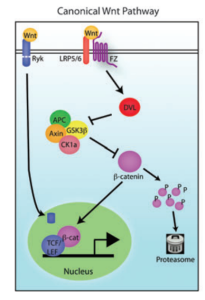
Michaud, J. L & Pourguie, O. (2013) an emerging role for Wnt and GSK3 signaling pathways in schizophrenia. Clinical Genetics 83, 511-517. Doi: 10.1111/cge.12111.
Wnt Signaling in Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is marked by a decrease of activity from a neurotransmitter (a chemical that neurons used to communicate with each other) called dopamine (DA). This is bad because DA indirectly helps to regulate the Wnt signaling pathway. As I mentioned before the destruction complex used to deactivate B-catenin contains a certain enzyme called GSK3B. Usually DA is able to indirectly activate this enzyme which helps keep the B-catenin levels under control. But when DA isn’t able to help out then B-catenin is overactive, and this can cause problems in the cell.
This is why many antipsychotic drugs that are used as a treatment for schizophrenia target DA levels. Specifically, they try to increase DA levels. When DA is more active it is better able to keep the GSK3B enzyme active and B-catenin inactive. This results in better control over the gene transcription in the nucleus so the cell can better control what proteins are being produced and run better.
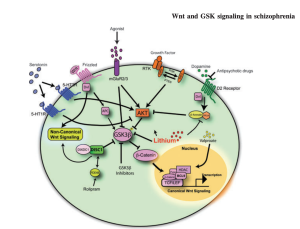
Michaud, J. L & Pourguie, O. (2013) an emerging role for Wnt and GSK3 signaling pathways in schizophrenia. Clinical Genetics 83, 511-517. Doi: 10.1111/cge.12111.
How to Help People with Schizophrenia
Unfortunately, there is not much that the everyday person can do if they have a loved one with schizophrenia. The most important thing is to offer your love and support for them when they are struggling. Try to encourage them to seek professional help from a psychiatrist. Of course, if there is an emergency where their health and safety is at risk then 911 should be contacted.
References
Michaud, J. L & Pourguie, O. (2013) an emerging role for Wnt and GSK3 signaling pathways in schizophrenia. Clinical Genetics 83, 511-517. Doi: 10.1111/cge.12111.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schizophrenia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354443
