
Glioblastoma is a type of cancer that starts with abnormal growth of cells in the brain or spinal cord that eventually turns into a tumor. Glioblastoma can occur at any age and symptoms may range from headaches, nausea and vomiting, blurred or double vision, and seizures. To test for glioblastoma certain tests can be performed such as a neurological exam, imaging tests like a positron emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, or performing a biopsy by removing a sample of the tumor tissue for testing.
Malignant brain tumor treatment could include surgery, radiotherapy, or intake of temozolamide (TMZ). Temozolamide works by crossing the Blood brain barrier, blocking DNA replication and cell proliferation, and functionally is an alkylating agent used to methylate DNA on the sixth position of guanine. For clarification malignant is not the same as bening, malignant is a cancerous faster growth that can reach the bloodstream to spread and wreak havoc on the body. Whereas, bening is a non cancerous slow growth that covers normal cells and doesn’t spread quickly to other parts of the body.
Pathway talk:
Figure 1 looks at the cAMP pathway which functions to regulate multiple cellular functions. To function a ligand binds to a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) activating the enzyme adenylyl cyclase to convert ATP to cAMP. cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) to inhibit tumor growth. This pathway may also be activated via Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDEi) to promote apoptosis.
Figure 2 focuses on the PI3K pathway functions to regulate cell differentiation, adhesion, motility, invasion, proliferation, and survival. This pathway is activated by binding the ligand to the RTK receptor causing dimerization and phosphorylation of RTK. Then PI3K is recruited to RTK via regulatory subunit p85 and activates p110. Then this subunit p110 converts PIP2 to PIP3, which is regulated by PTEN, PIP3 activates AKT so AKT can undergo phosphorylation and activation. AKT signals to other portions of the pathway such as mTOR to complete the functions listed above.
The last figure, figure 3, is the MAPK pathway the molecule binds to an RTK receptor which then goes to GRB2 and SOS, converting GDP on RAS to GTP on RAS ultimately leading to cell proliferation, survival, and migration. As seen in figure 3 NF1 functions to regulate the pathway by converting GTP to GDP and inactivating RAS.
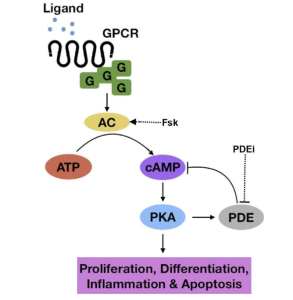
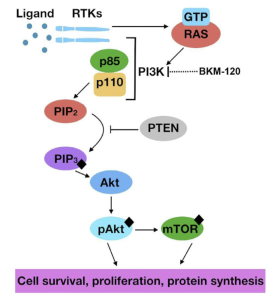
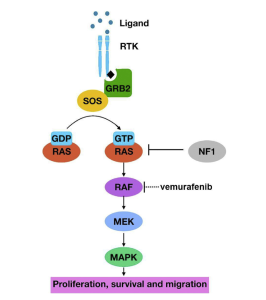
Figure 1: cAMP Pathway, Figure 2: PI3K pathway, Figure 3: MAPK pathway
In a new research study malignant tumor growth, also known as glioblastoma, impacts multiple signaling pathways such as MAPK, PI3K, and cAMP pathways. In tumor growth there is hyperactivation of MAPK and PI3K pathways well there is hyporegulation of cAMP pathways. Drug treatments that have been studied in the past target single pathways, however cross talk of pathways combination drug treatments should be the new focus for treatment of glioblastoma. There have also been studies focusing on convergence of CREB and how that could impact tumor growth. While glioblastoma is a treacherous disease to combat there has been more research to look at other possible solutions.
Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/glioblastoma/cdc-20350148
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30710631/