Cannabis on the Brain
The Endocannabinoid system regulates and controls many of our critical bodily functions such as learning, memory, emotional processing, sleep, temperature control, pain control, inflammatory and immune response, along with eating. [3] Therefore, the Endocannabinoid system has a major role in homeostasis and neuroplasticity of the brain and increased signaling is associated with reduced stress response, improved emotion regulation, and increased reward signaling.[1]
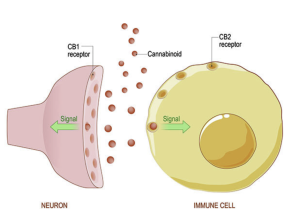
In the brain, the most populated receptors are the CB1 receptors as they function to regulate the levels and activity of most of the other neurotransmitters such as those that control hunger, temperature, or alertness. To stimulate the CB1 receptors there are molecules called Endocannabinoids that have a structural similarity to molecules of the cannabis plant. Interestingly enough, the first Endocannabinoid was named anandamide after the Sanskrit word ananda which means bliss. Therefore, with structural similarity to Endocannabinoids intake of cannabis can hijack the Endocannabinoid system.
As related to the Endocannabinoid system, THC in cannabis is a partial agonist with high affinities for both CB1 and CB2 receptors along with psychotropic effects. Overall THC has been shown to activate CB1 receptors in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, caudate/putamen, globes pall idus, substantial nigra, and cerebellum. Whereas, CBD is non-psychotropic effects and inhibits drug-seeking and self-administration in animal models. CBD does not bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors with high affinity. [1]
Fun fact: As we know that the hunger signal mainly comes from the hippocampus of the brain, cannabis intake stimulates CB1 receptors, which are high in the hippocampus, eliciting the “munchies” or need to consume more food for the consumer.
Positives for certain treatments
Two different components in cannabis are CBD and THC. CBD has been shown to be beneficial for Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral ischemia, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological disorders. THC has been approved for certain medical diagnoses usually including cancer or those individuals going through chemo treatment to elicit a hunger response and get them to eat more during treatment. Some examples of the pill form of THC offered are dronabinol, nabilone, and pure THC which is marketed as Marinol.
With the THC pill there is slow absorption that depends on the rate of gastric emptying before it has any psychoactive effects on the consumer whereas smoking there is direct entrance to the brain and the bloodstream. Along with this there is a higher risk of fatal overdose by swallowing too many THC pills.
As for the benefits of cannabis as a whole is that there is alleviation of chronic pain, inflammation, spasticity, and other conditions see in physical therapy practice. [1]
Negatives from long term usage
THC use in low doses may relieve anxiety however in higher doses can provoke anxiety and paranoia as responses are exacerbated by inhalation of cannabis. [4] Overall, THC has been shown to have adverse effects on executive functioning in the brain short-term therefore, effecting planning, reasoning, interference control, and problem solving. As for effects of chronic use of cannabis it has been found to negatively effect executive functioning and working memory along with processing speed. Certain parts of memory are impaired includes verbal learning, encoding, recall, and recognition. Some other notable impairments from cannabis use include effects on inhibition, impulsivity, and decision-making.
Why research is limited
Cannabis usage was at 183 million past year users in 2017 [1], however it is distributed at the local level depending on the state regulations it has been challenging for research companies to get ahold of the drug without going through a lot of barriers to obtain the substance. To research potential therapeutic cannabis usage researchers must obtain approval from a range of federal, state, or local agencies, institutions, or organizations along with applying for grant funding which goes with other barriers to research. In this last resource there is a more in-detail description of what process researchers need to go through. [5]
Cannabis intake can help to up-regulate the Endocannabinoid system through substance, however there are certain costs as previously talked about with usage. Other more natural ways to elicit the endocannabinoid system could be just as simple as exercise.