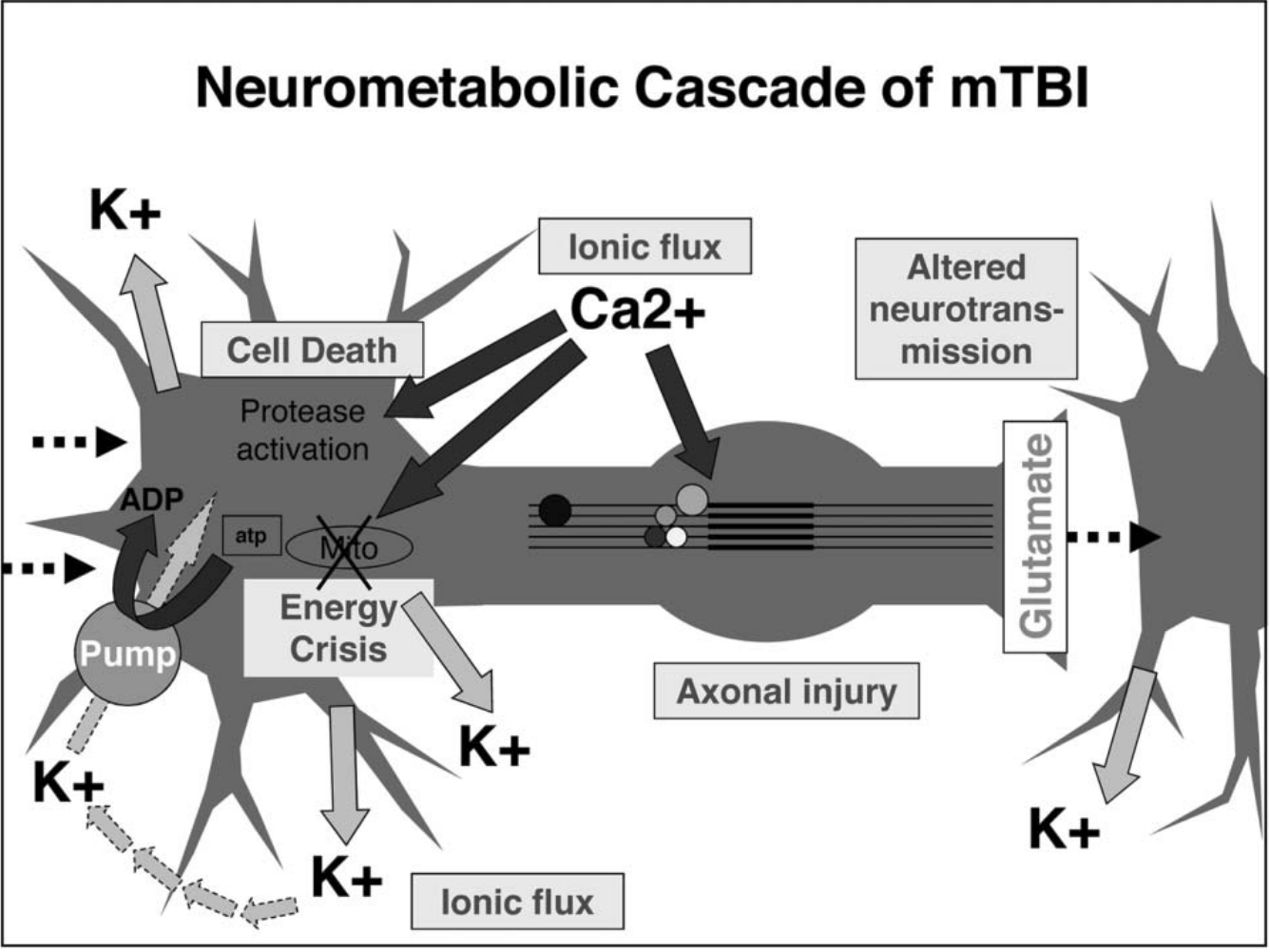
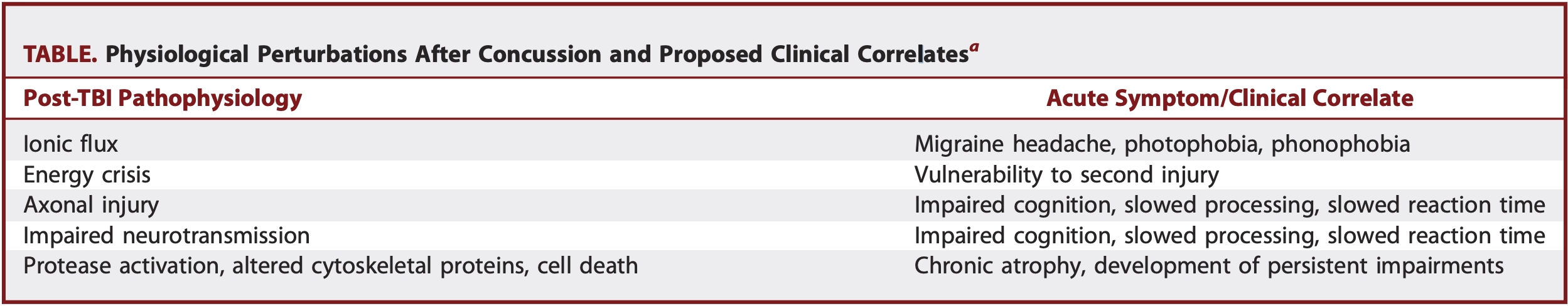
Introduction
Today’s topic is the treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that impacts memory, thinking, and behavior. It often leads to a progressive decline in all cognitive functions. Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most pressing health challenges facing aging populations today, no matter where in the world. With millions diagnosed, finding effective treatments is crucial not only for improving the quality of life for those diagnosed but also for easing the burden on caregivers, healthcare systems, and society as a whole.
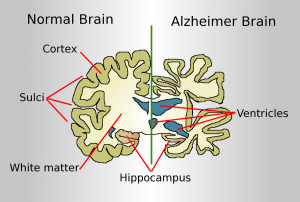
The search for Alzheimer’s treatments is connected to larger issues like the aging population, ethics of medical interventions, and healthcare resources. As life expectancy increases, Alzheimer’s disease is becoming more common. We need to make advancements in treatment for societal well-being. The ongoing research into Alzheimer’s connects to areas of neuroscience, biotechnology, and personalized medicine. Scientists are working to expand the boundaries of what we know about the brain and how diseases can be treated.
Treatments
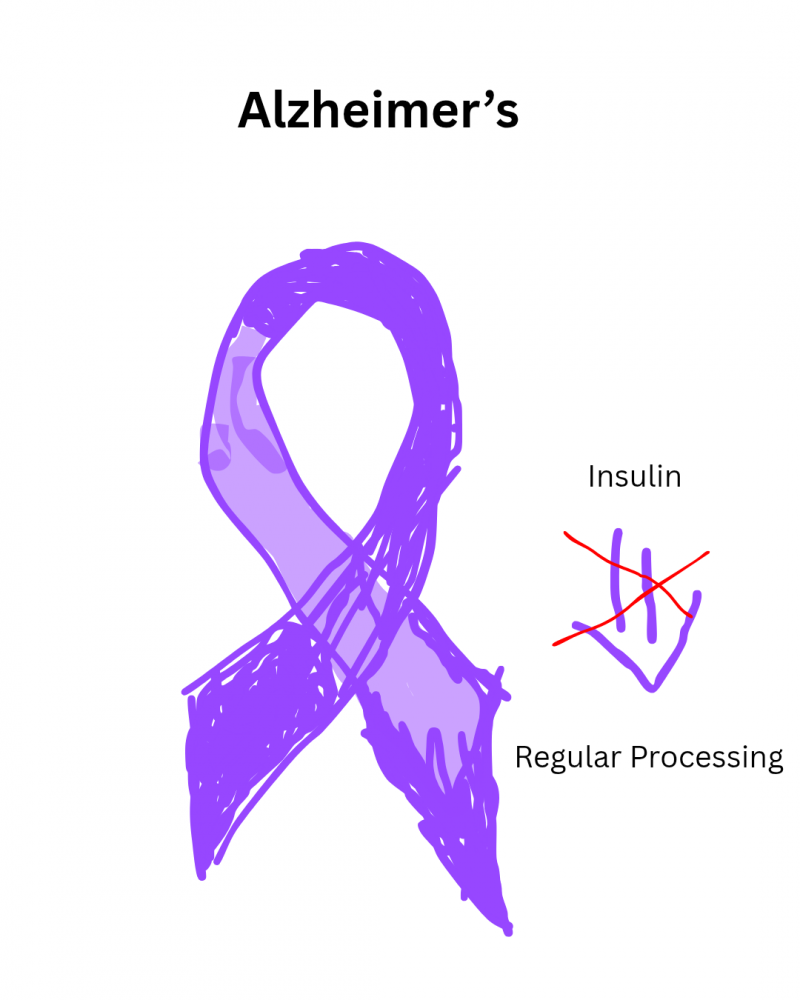
Alzheimer’s disease treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression. There is no cure. Medications like cholinesterase inhibitors (for example, Donepezil) and glutamate regulators (ex. Memantine) can help improve memory and cognitive function [1]. Newer treatments like monoclonal antibodies (ex. Aduhelm and Leqembi) target amyloid plaques specifically in the brain, stopping their growth [2]. Insulin treatments for Alzheimer’s, such as intranasal insulin, are being explored because insulin resistance in the brain contributes to cognitive decline, just like how insulin resistance in the body is a big factor in Type 2 diabetes. These treatments aim to enhance memory and cognitive function similarly to how insulin therapy helps manage glucose levels in diabetes. Lastly, GLP-1 agonists, like Ozempic, show possible promise for protecting brain cells and improving cognition [3]. Outside of medication, lifestyle changes like exercise, a healthy diet, and cognitive therapies can support brain health and well-being.
These findings note the challenge of Alzheimer’s disease. We are in need of finding treatments that can not only stop the degradation of the brain, but heal what damage has been done [4]. Exploring insulin therapies and GLP-1 agonists (like Ozempic) is causing researchers to shift focus to the brain’s metabolic processes, which may open up new avenues for slowing cognitive decline and improving quality of life for patients. These treatments provide hope for patients who haven’t responded well to existing medications.
The newer pathways for research further investigate the role of insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s, as well as exploring how GLP-1 agonists can protect neurons and improve brain health. They encourage the use of combination therapies, where metabolic treatments could be used alongside existing drugs or lifestyle interventions to create more care strategies [5]. This could lead to more effective treatments or preventive measures.
Societal Application
The topic of Alzheimer’s treatment definitely has an impact on everyday life and larger societal issues. This disease affects well-being of millions of people worldwide. As the global population ages, Alzheimer’s disease is becoming an increasingly intense concern because it strains healthcare systems and families who provide care for loved ones. Effective treatments could not only improve the lives of patients but also alleviate the emotional and financial burdens on caregivers.
Here are some questions to consider. How might advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment change our perceptions of aging? What if treatments targeting the brain’s metabolic processes, like insulin and GLP-1 therapies, could become as common as diabetes management? Could the future of Alzheimer’s care include personalized treatments based on genetic and metabolic factors?
The main message I want readers to remember is that while Alzheimer’s disease currently has no cure, research into treatments like insulin therapies, GLP-1 agonists, and amyloid-targeting drugs offer some hope for slowing progression and improving lives. These innovations not only provide new options for those with the disease but also open pathways for future treatment that could change how we approach aging and brain health.
References
[1] Podhorna, J., Winter, N., Zoebelein, H., & Perkins, T. (2020). Alzheimer’s Treatment: Real-World Physician Behavior Across Countries. Advances in Therapy, 37(2), 894–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01213-z
[2] Severe Alzheimer’s Disease Study Group, Winblad, B., Kilander, L., Eriksson, S., Minthon, L., & et al. (n.d.). Donepezil in patients with severe Alzheimer’s disease: double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study. The Lancet, 367(9516), 1057–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68350-5
[3] Liang, Y., Doré, V., Rowe, C. C., & Krishnadas, N. (2024). Clinical Evidence for GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports, 8(1), 777–789. https://doi.org/10.3233/ADR-230181
[4] Parvin, S., Nimmy, S. F., & Kamal, M. S. (n.d.). Convolutional neural network based data interpretable framework for Alzheimer’s treatment planning. Visual Computing for Industry Biomedicine, and Art, 7(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42492-024-00154-x
[5] Theisen, P. (2024). Alzheimer’s Association Board,of Directors. Early alzheimer’s detection can aid treatment, planning. Telegraph – Herald Retrieved from http://cordproxy.mnpals.net/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/newspapers/early-alzheimers-detection-can-aid-treatment/docview/3068907826/se-2



 Figure 1
Figure 1 Figure 2
Figure 2
 Figure 3
Figure 3 Figure 4
Figure 4 Figure 5
Figure 5