If you have ever had trouble sleeping, you most likely watched late-night television in order to fall asleep. The commercials televised in the wee hours of the morning often display miracle products, several being diets and weight loss supplements. These products often fail as obesity is a complex disorder caused by several factors. Recent studies have shown a correlation between the inflammation of the hypothalamus and obesity. The cause of this inflammation is still being examined, but one leading cause seems to be the impairment of leptin and insulin signaling.
Understanding the function of the hypothalamus in obesity is crucial for the development of a cure. Early lesion experiments revealed that alteration in the hypothalamic region of the brain resulted in changes in feeding behavior and energy expenditure. Two types of neurons are responsible for this regulation. AgRP neurons control food intake while POMC neurons decrease food intake and increase energy expenditure. Leptin and insulin play major roles in the homeostasis of both neurons. An improper balance of leptin and insulin or ineffective leptin and insulin signaling corresponds to an increase in food consumption and simultaneous decrease in energy expenditure. Studies have shown diets rich in saturated fatty acids cause activation of cytokines and inflammatory pathways, which disrupt leptin and insulin signaling in the hypothalamus. The activation inflammatory pathways lead to transcription of genes like SOCS3, leading to more cytokines and inflammatory signaling. This leads to the chemical hardwiring of the brain to eat more food, making losing weight a massive challenge. The figure below demonstrates some of the neurochemistry of obesity.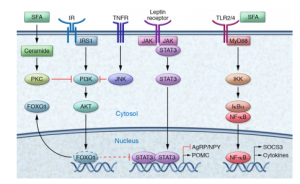
This research does however lead to several possible treatments of obesity. Administering medication that prevents the transcription of inflammatory genes and hinders cytokine and inflammatory pathway signaling are two viable treatment options. Several studies have shown using anti-inflammatory medication such as Tylenol can decrease weight gain. The simple solution would be to prevent over nutrition or limit saturated fatty acids. However, this may not be as simple as it appears. Currently cheapest and affordable foods, those purchased most frequently by the public, are high in sugars, carbohydrates, and fatty acids. Only individuals with money can afford to purchase fresh fruits and vegetables. This leads to a social and economic dilemma regarding weight gain and obesity. Furthermore, the human body was designed from an evolutionary standpoint. In other words, the ease at which food can be obtained and consumed today, compared to the hunter-gatherer lifestyle, raises the risk for obesity.
The issue of obesity is complex. Studies have shown a correlation between hypothalamus inflammation and the disease. It is hypothesized that inflammation occurs because of an imbalance or impaired signaling of leptin and insulin, leading to inflammatory responses. Treatments of obesity vary in their approach; however, mediation of inflammatory genes and pathways has shown promising results. Factors outside the physiologic domain must also be examined. Several economic and societal facto directly impact obesity. Understanding the complexity of the disease is imperative for one day finding a cure.
Sources
