Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease that causes difficultly with cognitive function, behavior, and day-to-day life functioning and it effects over 44 million people today. Although there has been extensive research over the years, there is little clarity when it comes to the cause of Alzheimer’s. In turn, there are no sure-fire ways to treat it or prevent it. But now, studies show the presence brain insulin resistance in those with Alzheimer’s.
Possible Causes of Alzheimer’s
Amyloid beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles have been known to be the main causes of Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Association notes that amyloid beta plaques and tangles lead to impaired cell signaling and inflammation. This leads to cell death.
Amyloid beta plaques are made up of smaller pieces known as beta-amyloid proteins. Shown in this image, amyloid beta plaques clump between neurons and cause disruption of cell signaling. 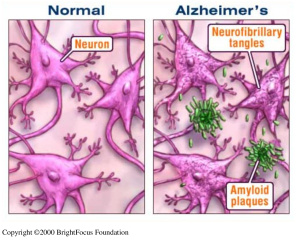
Insulin and Alzheimer’s
Insulin plays a role in the brain by altering, regulating, and protecting neurons. Insulin can protect neurons by stopping the amyloid beta plaques from building up. When inflammation is present, insulin resistance occurs. In this case, insulin cannot function properly, and the amount of insulin degrading enzymes decreases. Insulin degrading enzymes also degrades amyloid beta plaques. With decreased insulin degrading enzymes, amyloid beta plaques build up, causing cell death and Alzheimer’s symptoms. ¹
Inflammation
Inflammation can be caused by a poor unbalanced diet. Intake of too many saturated fats can lead to inflammation. While eating unsaturated fats and antioxidants can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress is caused by the presence of too many oxidants and not enough antioxidants. Antioxidants play a role in protecting tissue. But, in Alzheimer’s disease antioxidants are depleted and oxidative stress causes inflammation. ²
Cytokines are proteins to regulate inflammation. Continued inflammation of the brain causes cytokines to continually release. Cytokines will then allow peripheral immune cells to enter the brain creating a continual inflammatory response. Therefore, the presence of these pro-inflammatory cytokines will lead to insulin dysfunction.
Mediterranean Diet and Inflammation
The Mediterranean diet has been proven to have anti-inflammatory effects. As stated previously, eating a diet that consists of unsaturated fats versus saturated fats as well as adding antioxidants helps to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. The main source of fat comes from olive oil which is an unsaturated fat. This diet is also characterized as being high in antioxidants with a high amount of fruits and vegetables. It has then been shown that those who stick with the Mediterranean diet are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, a diet with a high intake of pro-inflammatory foods such as red meat, processed meats and fried foods has been shown to lead to cognitive decline. ³
What should we do?
As of right now, there is no way to reverse Alzheimer’s, but we can prevent it. Given the promising effects of the Mediterranean diet, it can be possible to prevent Alzheimer’s through diet. I believe the best course of action would be to catch insulin resistance early. Similar to screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, the same screening could be done in light of preventing Alzheimer’s. Essentially, preventing type 2 diabetes would be preventing Alzheimer’s. Treating type 2 diabetes would also be early intervention of Alzheimer’s by addressing insulin resistance.
- Akhtar, A., & Sah, S. P. (2020). Insulin signaling pathway and related molecules: Role in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochemistry international, 135, 104707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104707
- https://tissuerecovery.com/blogs/brain/improve-your-memory-by-reducing-oxidative-stress
- McGrattan, A. M., McGuinness, B., McKinley, M. C., Kee, F., Passmore, P., Woodside, J. V., & McEvoy, C. T. (2019). Diet and Inflammation in Cognitive Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Current nutrition reports, 8(2), 53–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-019-0271-4
