Artstract by Timea Vrabcová (using DALL.E)
Artstract by Timea Vrabcová (using DALL.E)
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that is characterized by a range of symptoms including delusions, hallucinations, disordered thinking, and abnormal behaviors. It is a chronic illness that typically appears in early adulthood and can have a significant impact on individual’s perception of reality [1]. While the exact cause of schizophrenia is not fully understood, recent studies have suggested a link between schizophrenia and the Wnt signaling pathway.
Symptoms
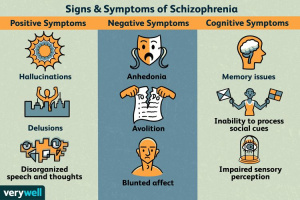
One of the hallmark symptoms of schizophrenia is the presence of hallucinations and delusions [2].
- Hallucinations = perceptual experiences that occur in the absence of external stimuli
- Delusions = fixed, false beliefs that are not based on reality
These symptoms can be extremely distressing and can interfere with a person’s ability to function in daily life. The exact neural mechanisms underlying these symptoms are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that they may result from abnormalities in the brain’s sensory processing systems, as well as abnormalities in the connectivity between different brain regions.
Causes
One of the primary causes of schizophrenia is the dysfunction of dopamine signaling in the brain. This leads to an overstimulation of dopamine receptors, which causes an imbalance in the communication between the neurons.
Another significant factor in schizophrenia is the reduction in the size of certain brain structures, including the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. The hippocampus is responsible for memory formation and retrieval, while the prefrontal cortex controls decision-making, planning, and attention.
One of the prevailing theories of schizophrenia is that it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors such as prenatal exposure to viruses, early childhood trauma, and drug use may also increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
How is Schizophrenia Studied?
The brain abnormalities associated with schizophrenia have been extensively studied using advanced imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). These studies have shown that people with schizophrenia have structural and functional abnormalities in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.
- Wnt Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathway is a complex network of proteins that play a critical role in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cell differentiation [3]. The pathway is activated by the binding of Wnt ligands to cell surface receptors, leading to the activation of downstream signaling pathways. Alterations in Wnt signaling may contribute to the dysfunction of neurotransmitter systems involved in schizophrenia, such as dopamine and glutamate and disrupt emotional and cognitive processing [4].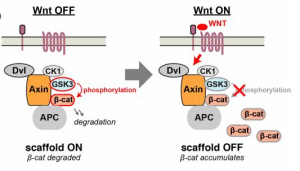
- Animal Models [5]
Studies investigating the development of schizophrenia use animal models, especially mice and rats due to their complex social behavior and genetic similarity to humans [6]. Blocking the Wnt pathway during brain development led to the development of schizophrenia-like symptoms in mice. Specifically, the mice exhibited deficits in working memory, social behavior, and sensory gating, which are all symptoms commonly seen in schizophrenia. These findings provide further evidence of a link between Wnt signaling and schizophrenia.
What is the Treatment for Schizophrenia?
The most commonly used treatments are antipsychotic medications, which work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. While these medications can be effective in reducing the positive symptoms of schizophrenia such as hallucinations and delusions, they may not be effective for all individuals and can cause significant side effects, such as weight gain, sedation, and movement disorders. Other treatments that may be helpful for people with schizophrenia include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy, which can help individuals and their families manage the condition and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which Wnt signaling contributes to schizophrenia and to develop effective treatments for this debilitating condition. By increasing awareness and understanding of schizophrenia, we can help to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness and improve outcomes for those affected by this challenging disorder.
Sources
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/schizophrenia-sign-symptoms-5095511
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3967064/#:~:text=Axin%2C%20a%20key%20component%20of,6%20and%20facilitates%20the%20recruitment ▲
- doi: 10.1111/cge.12111
- https://elifesciences.org/articles/54020
- https://www.cyagen.com/us/en/community/technical-bulletin/mice-vs-rats.html