:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-sign-symptoms-5095511_final-57a52853a10c4edcb4bd6a3b31f041ea.jpg)
A. What is Schizophrenia
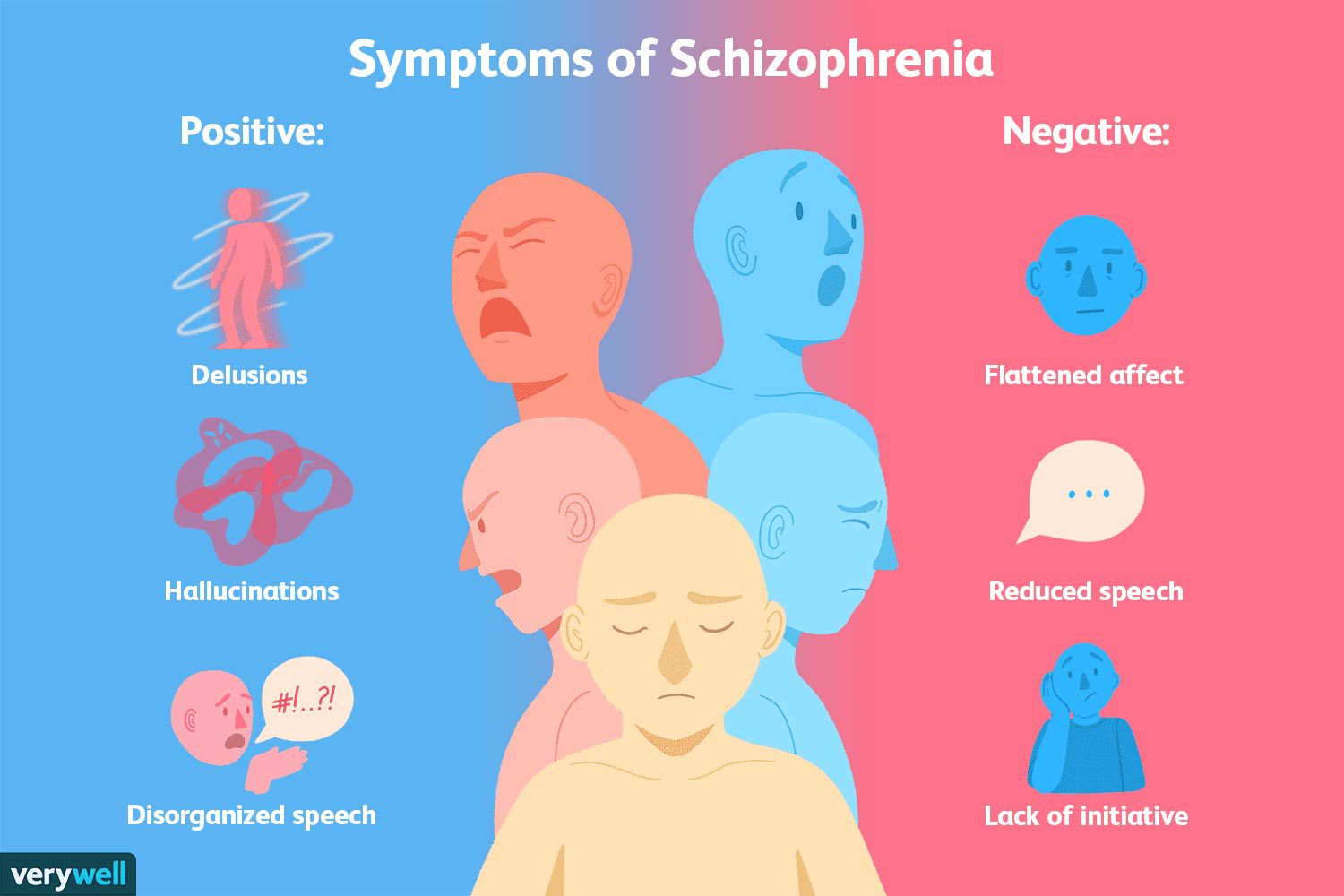
Schizophrenia is a complex neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by disturbances in cognition, perception, and behavior. While the precise etiology of schizophrenia remains elusive, growing evidence suggests that dysregulation of various signaling pathways may contribute to its development. Schizophrenia can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status.
B. The Paper
An Emerging Role for Wnt and GSK3 Signaling Pathways in Schizophrenia explores the increasingly recognized involvement of the Wnt and GSK3 (glycogen synthase kinase 3) signaling pathways in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, offering insights into potential mechanisms underlying the disorder.
C. Wnt
The paper begins by providing an overview of the Wnt signaling pathway, which plays critical roles in neurodevelopment, synaptic plasticity, and adult neurogenesis. Singh discusses how aberrant Wnt signaling has been implicated in schizophrenia, with alterations observed in Wnt ligands, receptors, and downstream effectors in postmortem brain studies and animal models of the disorder. Dysfunctional Wnt signaling may disrupt neural circuitry and synaptic connectivity, contributing to the cognitive and behavioral deficits observed in schizophrenia.
D. GSK3 and its relation to Wnt
Furthermore, the paper explores the role of GSK3, a key regulator of the Wnt pathway, in schizophrenia pathogenesis. Dysregulated GSK3 activity has been implicated in various aspects of schizophrenia, including neurodevelopmental abnormalities, neurotransmitter dysregulation, and synaptic dysfunction. GSK3 dysregulation may contribute to the imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission observed in schizophrenia, leading to altered synaptic plasticity and neuronal communication.
Moreover, the paper discusses the potential interactions between the Wnt and GSK3 signaling pathways in schizophrenia. Singh highlights how GSK3 can modulate Wnt signaling by phosphorylating key components of the pathway, thereby influencing downstream transcriptional responses and cellular processes. Dysregulated crosstalk between Wnt and GSK3 signaling may disrupt neurodevelopmental processes and synaptic function, ultimately contributing to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
E. Treatment
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/schizophrenia-treatments-2330662-86632e6754d0472bb5c2891d6eb94bcd.png)
The paper concludes by underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting Wnt and GSK3 signaling pathways in schizophrenia. Singh discusses preclinical and clinical studies investigating pharmacological agents that modulate Wnt signaling or inhibit GSK3 activity as potential treatments for schizophrenia. By restoring the balance of Wnt and GSK3 signaling, these interventions may offer novel therapeutic strategies for ameliorating the cognitive and behavioral symptoms of schizophrenia.
In the traditional setting, schizophrenia is treated with antipsychotics with the help of psychotherapy counseling.