The Story of BDNF and Alzheimer’s
The human brain is constantly adapting to experience. Everyday it builds new connections, repairs damage, and keeps signaling steady. When the brain’s systems start failing, signals slow and memory fades. This is what happens as Alzheimer’s disease develops. An important protein in this process is called brain derived neurotropic factor, or BDNF. This is a growth factor in the central nervous system that supports neuron growth, survival, signaling, and promotes synaptic plasticity, which we need for learning, memory, and emotional regulation [1]. BDNF acts by binding to a receptor on neurons, called TRKB, triggering various signaling pathways that promote cell survival and functional signaling [2]. High BDNF levels are healthy and strengthen the brain, whereas low BDNF levels lead to weak neurons and foggy memory.
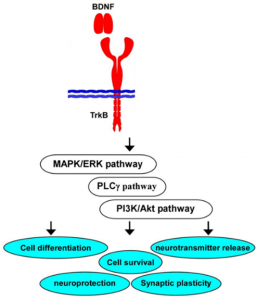
This image shows which pathways are activated by BDNF binding and the various effects it supports in the brain [5].
Growth Factors
Growth factors, in general, have a significant role in brain health. They support many brain mechanisms, such as insulin signaling in the brain. Many people are aware of insulin’s role in relation to blood sugar, but it is also incredibly important to the brain. Abnormal insulin signaling in the brain can lead to poor glucose metabolism (how the brain gets energy), neuron death, and Alzheimer’s disease. This means that the brain loses energy and its repair mechanisms, resulting in amyloid-B accumulation, inflammation, and synaptic loss. Insulin signaling pathways overlap with growth factor signaling pathways, like those activated by BDNF. Growth factors counter these effects of poor insulin signaling, by reducing inflammatory signaling and protecting neurons from amyloid-B toxicity, common in Alzheimer’s disease [3].
Influencing Growth Factors
Growth factors can be influenced by lifestyle and habits. Scientists have found that activities like regular exercise, quality sleep, social interaction, cognitive engagement, and diets rich in omega-3 fats and antioxidant compounds can increase BDNF levels. On the flip side, chronic stress, sleep deprivation, high saturated fats, refined sugars, and depression all correlate with lower BDNF production. Therefore, we can influence the pathways in the brain that support resilience.
This video from integrative natropathologist and pharmacist, Vanita Dahia, further explains the connection between BDNF and Alzheimer’s, and some methods to promote BDNF levels.
Brain Repair?
But what about people who are already experiencing neurodegeneration, where lifestyle changes might not be enough to restore lost neuron connections? Researchers are investigating therapeutic strategies to boost growth factor signaling in the brain. One promising approach is gene therapy. Vectors carry genes that code for growth factors directly into brain tissue. These genes will produce growth factors long-term within neurons [4]. Early clinical trials suggest this approach can promote neuron survival and slow Alzheimer’s disease progression. Another strategy uses intranasal sprays, delivering growth factors from the nose directly into the brain. This path avoids the bloodstream, which reduces side effects [7]. Both approaches remain experimental and no growth factor therapy has been approved as treatment for Alzheimer’s, though these methods are hopeful.
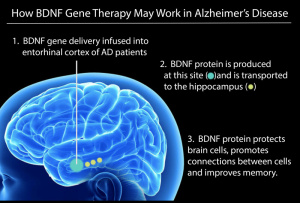
This image describes the process of BDNF gene therapy, and how it can be used to repair the brain in those with Alzheimer’s disease [6].
Conclusion
Therefore, the story of BDNF and Alzheimer’s teaches us that brain health includes a complex signaling networks that include insulin, growth factors, and cellular energy systems. It also shows us that the brain’s vulnerability to disease uses the same systems that support its resilience. The brain responds to signals from growth factors, like BDNF, which are influenced by lifestyle choices. Advanced therapies offer hope for repairing damage at the cellular level, but everyday habits are important too. With each discovery about insulin, BDNF, and neurodegeneration, we gain a clearer picture of how to protect the brain and growth factor therapies may be able to repair the brain.
A concise summary can be viewed at http://neurochemistry2026.pbworks.com/w/page/163250862/BDNF%20and%20GFs%20as%20AD%20therapy .
References
[1] Bathina, Siresha & Das, Undurti. 2015. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical Implications. Archives of medical science : AMS. 11. 1164-1178. 10.5114/aoms.2015.56342.
[2] Colucci-D’Amato, L., Speranza, L., & Volpicelli, F. 2020. Neurotrophic Factor BDNF, Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential in Depression, Neurodegeneration and Brain Cancer. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(20), 7777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207777
[3] Akhtar, A., & Sah, S. P. 2020. Insulin signaling pathway and related molecules: Role in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochemistry International, 135, 104707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104707
[4] Tuszynski M. H. 2024. Growth Factor Gene Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD, 101(s1), S433–S441. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-240545
[5] Numakawa, T., & Kajihara, R. 2023. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the pathogenesis of stress-related brain diseases. Frontiers. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/molecular-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnmol.2023.1247422/full
[6] BDNF. ACROBiosystems. https://www.acrobiosystems.com/category/target-protein/bdnf?msclkid=04fd2c7c9c4e13fc84bc45efc20fee07&utm_source=bing&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=PL.-CYTOK%2BTARGETS.-%5BUSA%5D.-DSA-Bing&utm_term=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.acrobiosystems.com%2Fcategory%2Ftarget-protein%2Fbdnf&utm_content=CYTOK%2BTARGETS.-CUSTOM
[7] Cattaneo, A., Capsoni, S., & Paoletti, F. 2008. Towards non invasive nerve growth factor therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease : JAD, 15(2), 255–283. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2008-15210
