CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors are G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) that are mostly found in the central nervous system (CNS) but can also be found in peripheral tissues and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They are found on presynaptic neurons. These receptors play an essential role in learning and memory and synaptic plasticity. When these receptors are coupled with Gi/o proteins, they inhibit adenylyl cyclase, and when they are coupled with Gs proteins, they stimulate adenylyl cyclase. [1]
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors can be found in cells and tissues of the immune system and are typically only expressed when there is active inflammation in the body. They are typically localized to microglia which have anti-inflammatory effects. [2]
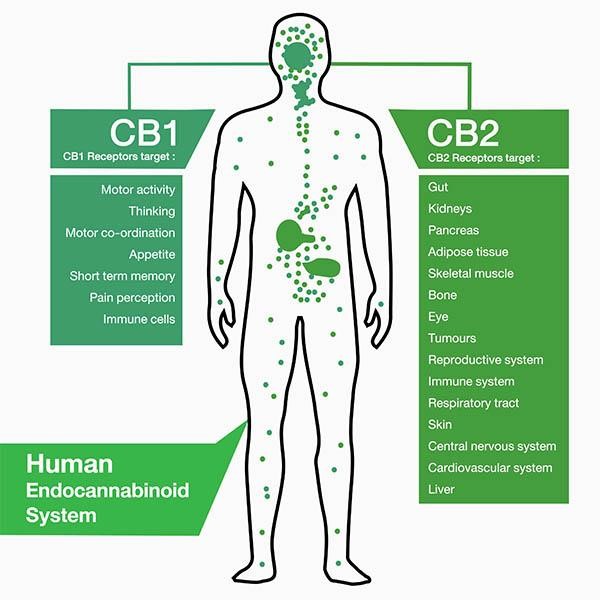
Endocannabinoid System
Endocannabinoids are natural agonists for the CB1 and CB2 receptors. They are triggered by the release of calcium at the postsynaptic neuron. The endocannabinoid system controls mood, pain perception, and learning and memory. It can also provide protection against traumatic brain injury (TBI) and can repair neurodegeneration. Learning and memory comes into play with the endocannabinoid system as it plays a key role in modulating synaptic plasticity—the ability of the brain to change connections between neurons. [4]

THC vs CBD
CBD and THC are both derived from cannabis plants and have very similar molecular structures. The primary difference between the two is that THC is psychoactive and CBD is non-psychoactive. CBD products are federally legal whereas THC is not and is only legal in some states. CBD is also not considered addictive whereas THC can lead to addiction (about 30% of marijuana users become addicted). [6]
Cannabis as Treatment for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Multiple Sclerosis
Cannabis, particularly THC, can have positive effects on spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis (MS). Sativex, a spray that is ingested through the mouth or nose and is composed of both CBD and THC, has been used to treat MS. This treatment acts on both CB1 and CB2 receptors to reduce both pain and inflammation.
Huntington’s Disease
In Huntington’s disease, CB1 receptor expression is reduced which decreases motor performance. To treat Huntington’s disease, CB1 can be activated to reduce symptoms.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is partially characterized by dementia and synthetic endocannabinoids may better dementia symptoms in AD. AD is believed to be caused by amyloid-beta plaques and tau protein phosphorylation. Activation of both CB1 and CB2 receptors can provide protection against amyloid-beta toxicity, and CBD can reduce tau protein phosphorylation. [4]

Ethical Concerns in Research
Since cannabis is not federally legal and only legal in some states, research participants could be at legal risk if their identity is disclosed. Another issue is impairment of participants and making sure that researchers are getting informed consent. Ensuring that consent is received prior to any ingestion of the drug is imperative for ethics of the study. Individuals’ ability to understand and make sound decisions could be impaired under the influence of cannabis. [8]

References
[1] Howlett, A. C., Blume, L. C., & Dalton, G. D. (2010). CB(1) cannabinoid receptors and their associated proteins. Current medicinal chemistry, 17(14), 1382–1393. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710790980023
[2] Bie, B., Wu, J., Foss, J. F., & Naguib, M. (2018). An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Current opinion in anaesthesiology, 31(4), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000616
[3] What is the Endocannabinoid System? | Sona Pharmacy + Clinic. (2020, April 1). https://sonapharmacy.com/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system/
[4] Kendall, D. A. & Yudowski, G. A. (2017). Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 10(294). doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00294
[5] Goldberg, Ian. (March 2, 2023). Cannabis use and its effects on mood disorders | Talkiatry. Retrieved April 29, 2024, from https://www.talkiatry.com/blog/cannabis-use-and-its-effects-on-mood-disorders
[6] Center, L. H. T. (2023, November 15). CBD vs THC: Learn the Differences. La Hacienda. https://www.lahacienda.com/blog/cbd-vs-thc-learn-the-differences
[7] CDC. (2023, March 1). What We Know about Marijuana. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/marijuana/featured-topics/what-we-know-about-marijuana.html
[8] Fitzgerald, Kelly. (n.d.) Research and Cannabis: Ethical Research in a Changing Regulatory Landscape. Retrieved April 29, 2024, from https://www.wcgclinical.com/insights/research-and-cannabis-ethical-research-in-a-changing-regulatory-landscape/
[9] Corder, Katie-Leigh. (August 23, 2018). How UNC Researchers are Studying Cannabis. https://www.unco.edu/news/articles/unc-cannabis-research-projects.aspx
