Autism is yet another condition we discussed in class that I was not complete familiar with. I have met several people with autism of varying severity but I never really knew what may have caused it or what exactly was going wrong.
It turns out that my initial impression that autism was just one condition was incorrect. It turns out that autism is what is called a spectrum disorder meaning that it is several different pathways with similar outcomes combined to result in one condition. I was very surprised to find that so many different pathways were contributing to the symptoms typical of autism. Some neurotransmitters and receptors are present in smaller numbers than usual while chemicals leading to oxidative stress are at higher levels than usual.
The causes for autism seem to be a little hazy but genetics definitely seems to affect whether or not one develops autism. A genetic predisposition does not, however, mean that one will develop autism. Other environmental factors known as xenobiotics seem to also contribute to autism. Xenobiotics are basically anything put into your body that isn’t either made there or used fr nutritional purposes. Autism is generally diagnosed before the age of 3 or 4 and it is thought that those with the genetic predisposition that are then also exposed to some set of environmental factors very early in life will then develop autism.
It was widely believed for a period of time that infant vaccination was contributing to an increase in autism diagnosis. This belief was later found to be untrue but it is still believed that there is some outside contributing factor to the development of autism. Another possible reason for the increase in the diagnosis of autism is the awareness of both doctors and parents. Parents who are aware of the symptoms of autism are more likely to bring their child in for diagnosis where before the symptoms were widely known mild cases of autism may have just been written off as a little odd.
Researchers also believe that it may soon be possible to in part prevent autism in infants. They believe that identifying those with the genetic predisposition for autism will help parents and doctors avoid any adverse environmental factors as well as begin social therapies at a very early age while the parts of the brain responsible for social interaction are still extremely plastic. This combination is hoped to possible prevent some cases of autism and significantly decrease the severity of others.
Ethanol: A matter of perception?
As we discussed ethanol this week in class I began to realize that the problem with alcohol in our country is truly a problem of perception. I’m not saying that we perceive the problem as larger than it is, but I do believe that our perception of alcohol as well as our perception of those who use it in excess is contributing to the problem.
Under aged drinking is obviously a problem we experience on a regular basis. It is rampant in colleges, universities and many high schools across the country and it seems that when those who are under age as well as those in college drink to excess when they have the opportunity. Solutions range from stricter enforcement to a lower drinking age to a flat out prohibition but I think our problem has a simpler solution. Change the perception of alcohol. Growing up you hear from your parents that alcohol is for adults and that you should never drink it until you are an adult. Right away you get rebellion and a desire to be an adult driving under aged people to want to drink. Next you have the Jersey Shore and other shows and movies that show people getting completely hammered and having tons of fun doing it. This sends the message that the purpose of drinking alcohol is to get completely smashed. If we could change how the consumption of alcohol is portrayed both in the home and in the media I think the urge to drink and drink to excess would decrease among under aged people.
Habitual and excessive drinking can also lead to the other perception I consider to be incorrect. Most of society view alcoholics as lazy slobs who are running away from their problems but chose not to help themselves. While it may be true that the initial drinking may have been in response to emotional stress, it is not likely the reason they continue to drink. Alcoholics develop an addiction much like any other drug addict. Ethanol affects many pathways in the brain some of which cause the lowering of inhibitions and slowing of cognition. Ethanol also causes the release of dopamine, the “happy” neurotransmitter, in regions of the brain that are related to behavior reinforcement. So just like your dog doing a trick to get a biscuit, alcoholics drink to get that rush of dopamine. They should be treated just like any other addict. Many alcoholics do not seek help because of the social stigma attached to alcoholism. If they were encouraged to get help and praised for getting healthy like those with other addictions they would likely be more receptive to help.
If these perceptions about alcohol and its use could be altered then I believe we would see a shift in the way it is consumed without have to change laws. Other countries have similar laws in place but do not experience the same problems because drinking alcohol is portrayed as something that is normal in moderation and is not meant to be consumed exclusively by adults in a party type setting.
Bipolar: You may not have even known.
Before our discussion of bipolar disease in class I always imagined people who would seem fine one second and then have a huge, angry outburst. I genuinely believed that the emotions of people with bipolar could turn on a dime. I was once again proven to be wrong.
Bipolar disease is long periods of depression followed by long periods of mania or hypomania (an emotional state in which the subject is extremely happy but not manic). Hypomania is more difficult to diagnose because it seems more like a peppy personality than a chemical imbalance. The exact pathway causing this imbalance is not known which makes you start to wonder how exactly medications are made and prescribed for this disease.
The most common method of prescription for bipolar is called rational pharmacy. Basically what this means is the doctor will prescribe the patient a drug depending on the symptoms they are experiencing at the time. If the patient is exhibiting depressive behavior they are prescribed an antidepressant and vice versa. There are very few drugs that are very effective for the manic stages of bipolar so it is the depression that is primarily treated in most patients anyway. This method often requires trial and error which can cause patients to be without proper medication until the correct mix of medications is found.
I find this fact to be a rather unfortunate one, but despite not having any idea what the cause of the disease is or how exactly to treat it there are many people who are very well known and constantly in the public eye who deal with bipolar without letting on that they have it. Some of these people include Russell Brand, Robert Downey Jr., Mel Gibson, Amy Winehouse, and Catherine Zeta-Jones.
Concussion: An unknown threat.
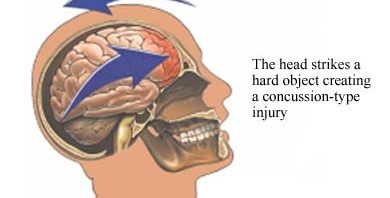
I am, like many other people, a student athlete. I have been playing rugby since I was 14 years old and the topic discussed this week in class took me quite by surprise. As an athlete at the age of 22 still engaged in a full contact sport I had no idea what exactly what a concussion was. I have myself suffered from a concussion on more than one occasion but I never thought very of them. I had always had the impression that they were sort of like a small brain bruise. Painful and annoying, but temporary with no lasting effects. I could not have been more wrong!
When you suffer a blow to the head or your head is caused to stop suddenly your brain also receives much of that force. This force causes the brain to move, stretching neurons. As the neurons are stretched various neurotransmitters effectively get squeezed out of them, sort of like twisting and stretching a wet wash cloth. The neurotransmitters that are rapidly released can cause swelling, increased blood flow, and even minor cell death. It also can cause confusion when signals are being sent through the injured part of the brain. These are what cause the characteristic headache, nausea, and mild amnesia associated with concussion.
That information alone changed my view on concussions enormously but there was even more to learn. The imbalance of neurotransmitters is not something that the brain can clear up quickly. Residual imbalances can last for weeks and recovery time varies depending on the person. During the recovery period those who have suffered a concussion should not only cease physical activity until cleared by a doctor but they should also limit the strain they put on their brain academically. After a concussion strenuous use of the brain like reading for extended periods of time can exacerbate the problem and cause headaches. Children take more time to recover from concussions than adults do which I thought would have been the other way around. Also if an athlete returns to play before the concussion has healed completely there is a significantly greater chance that they will suffer another, more severe concussion. There is also a chance that the athlete could suffer a very rare injury called second impact syndrome which can cause death within minutes of the second impact.
As an athlete who has participated in a contact sport for many years I felt that I should have been more aware of what exactly a concussion was. Having suffered multiple myself, one of which was rather severe (my nose was broken and two of my front teeth were knocked out), I would have liked to know that perhaps I shouldn’t have been doing some of the things I did afterwards. The concussion occurred on a Sunday afternoon and I was back in school on Tuesday and back at practice the following Monday. The rule for my league was I only had to sit for a week so long as my doctor cleared me and I felt OK to play. At the time I felt just fine but I feel like I may have made a different decision if I had known more about what was going on.
The MAPK Pathway
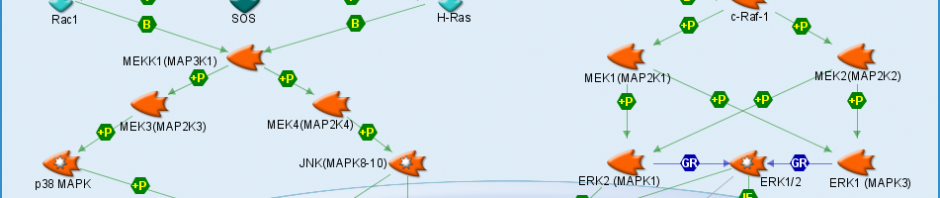
The MAPK pathway is incredibly important in our brain. Its functions range from cell growth and development to inflammation and cell death. This pathway is incredibly large and is responsible for many different things. Diseases like Parkinson’s and ALS have been linked to a disruption in the MAPK pathway leading to oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress occurs when oxidant by products from certain processes reach levels that are too high for cells to deal with. The stress placed on the cells can be relieved but if it is not it affects how well they are able to function and can even lead to the death of the cell. It is believed that those with neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and ALS are experiencing motor neuron deterioration due to oxidative stress.
Targeting the MAPK pathway to fix this is problematic. Because MAPK is important to so many other processes it is almost impossible to alter it in a way that would prevent Parkinson’s or ALS and not cause some other problem in a different part of the pathway. The use of stem cell therapy has been used in an attempt to replace the lost motor neurons. This treatment appeared to be working for a time as the stem cells developed into new motor neurons but shortly afterwards the oxidative stress caused those neurons to degenerate just as the first ones did.
Neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and ALS are crippling to those who have it as well as those around them. Research is trying to find ways to make drugs that will target extremely specific receptors in the hope that being able to do so will make treating diseases like this possible when it has been impossible in the past. The number of important function performed by the MAPK pathway is too large to try and alter it without very target specific drugs.
The following is a link to a diagram of the MAPK pathway: http://www.avivasysbio.com/research-areas/mapk-signaling-pathway
Alzheimer’s Disease: Is junk food putting up road blocks in our brains?
We all know that sweets and fast food are bad for our health. They rot our teeth, add inches everywhere we don’t want them, clog our arteries, and put stress on our heart, but do they also affect our brain health? Current research is suggesting that yes, eating an unhealthy diet can, in fact, cause problems for our mental health.
Many of us are aware of the increasing rate of type II diabetes in the U.S. Type II, unlike type I, is caused by insulin resistance. Basically insulin is responsible for getting glucose into cells to be used for energy. When your body becomes resistant to insulin the glucose is not properly transported. Because the glucose is not reaching the cells your body thinks it still needs that energy so your liver produces even more glucose into your blood. Again the glucose cannot be taken anywhere so it builds up in the blood, a condition called hyperglycemia. This condition can be managed relatively easily with medication. What was not known about insulin resistance until just recently was that it can also occur in the brain.
Glucose is the primary form of energy used by the brain. Researchers are finding that in Alzheimer’s disease there is reduced use of glucose in parts of the brain. If the brain cells aren’t using as much energy then they are not working as well as they should be. It is believed that brain cells are also capable of developing insulin resistance so glucose is not properly transported to the cells that need it to function correctly. This is what is believed to be causing the progressive memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s.
If insulin resistance is such a large part of two very common problems what causes it to happen and how can it be avoided? Insulin receptors can become less sensitive to insulin levels if insulin levels are chronically high. Since cells only need as much glucose as they need to produce energy the insulin receptors need to become less sensitive if there is regularly more insulin present than the cells need to import glucose. This occurs when a diet is full of unnecessary sugars and fats that are most often present in sweets, sodas, and fast food. If this life style is maintained overtime the insulin receptors can become resistant to insulin and that can lead to type II diabetes and even Alzheimer’s disease.
I am not trying to say that if you indulge in a Big Mac or a can of your favorite soda from time to time you are going to develop diabetes or Alzheimer’s disease. Moderation is always key and an unhealthy diet does not guarantee that you will develop one of these conditions. Awareness of how your food choices will affect you now, tomorrow, and 20 years down the road is important and knowing the cause of diseases like these can help in future treatment options as well as prevention.
Medical Marijuana: Relief without a lighter?
The legal use of marijuana has been a hot topic in the U.S. for years. The primary argument for its use is that it has shown to be highly effective for those suffering severe pain. The use of medical marijuana is legal in many states, but is the use of medical marijuana truly necessary? Are the benefits of its use greater than its drawbacks? What if there was another option?
Marijuana works as a pain killer by working in a system called the endocannabinoid system. When compounds like cannabis are present in our body they bind to our neurons and decrease the amount chemicals that are released from these neurons. At the site of an injury or other source of pain the chemicals being limited are those that would cause sensitivity and inflammation. This is why medical marijuana is used to reduce pain and why it is so effective.
The obvious drawback to the use of marijuana is its psychotropic or mood and behavior altering effects on those using it. THC is the primary chemical found in marijuana. While it does relieve pain it also causes mood and behavior changes as well as other side effects including increased appetite often referred to as “the munchies”. A synthetic form of THC is available as a prescription in both the U.S. and Canada under the name Marinol.
A lesser known component of cannabis is Cannabidiol. Cannabidiol makes up about 40% of the compounds present in cannabis and functions in much the same way as THC. The major difference between the two is that Cannabidiol does not have the psychotropic effects of THC.
Knowing this is there truly any reason for the use of medical marijuana? The main components present in marijuana can be made synthetically in a lab and the non-psychotropic component can be separated from the psychotropic one meaning we can have the pain relieving effects of marijuana without any other side effects. Also if the medically significant components or marijuana are produced in a lab instead of being grown either in or outside of the United States the rate of abuse would likely decrease because anyone with possession of the plant based form of the drug would be in violation of the law. Also Cannabidiol would not be abused as a recreational prescription because it lacks the psychotropic effects sought by a recreational user. On a whole the use of medical marijuana is becoming unnecessary as more is being discovered about the chemical components and how they can be synthesized in a laboratory setting. In addition the synthesis of these drugs would make distribution, possession, and growing laws much simpler for those truly using the drug for medical purposes and for law enforcement. On a whole unless you are looking for a high there is no reason for the legalization of marijuana.
Neurochemistry Reflections
For those of you who can’t read 0.2 size font, the molecule shown in the featured picture is oxytocin. Eh? Eh? Get it?
Anyway, this course truly was everything I wanted and more. Unlike many of my classmates, I took Neurochemistry as basically the only elective I will be able to take in my undergraduate career. (Filling requirements for a chemistry major, a math major, and all the liberal arts core classes that a Concordia degree requires takes quite a bit of time to complete without overloading or going insane.) Actually, during my sophomore and junior years I considered dropping my math major to pursue more coursework in neuroscience, thinking that ultimately I’d go to graduate school for neurochemistry. Thus, discovering that the neurochemistry class offered here fit into my schedule my senior year, I was pretty darn ecstatic. However, I noticed that the class did not have a lab associated with it which was different from any science class I had taken, so I was a bit wary of what would be in store, especially since it was attributed as a senior capstone class. Capstone classes are, by definition, writing-heavy classes, and writing papers is not one of my favorite things to do, to put it lightly.

Despite my pre-semester concerns, however, this class turned out to be not only enjoyable, but extremely useful as well. I think that one of the weaknesses of the chemistry classes I have taken thus far is that they don’t take much time to connect the course material with what is actually happening in the field. Granted, most just don’t have the time to do this due to the tremendous amount of material that needs to be covered in a short time, but it is still very important to those that are going to do research at any time in their chemistry careers. From my summer undergraduate research program, I have discovered that reading these sorts of articles comprises an almost unbelievable portion of one’s time spent in research. A person needs to gather foundational information on the material and instrumentation to develop a method for their project, make sure that someone hasn’t already done the same experiment, and in some cases search literature for an initial topic that is important to the scientific community. This course not only encouraged reading scientific articles and reviews, but the required reading was solely these articles. Scientific journals are a very different form of writing than most prose, and in order to read them fairly quickly and effectively, a person needs practice. With our weekly journal articles, we both gained familiarity with this style and learned how best to go about dealing with the information presented. Each week we worked together to understand the overall message of the article, determine what was important and what was trivial, and communicate our findings with the non-science world. This last portion is the reason for this blog series, and definitely an important step in the research process; although it’s necessary to effectively communicate with the rest of the scientific community, it’s extremely important to share our progress with the rest of society to gain support and feedback to continue or reevaluate different aspects of a project. Working within a fairly specific group of probably like-minded people, one’s perspective can easily become skewed; communication with other groups helps to ground oneself.

This class has been so beneficial to me that I would suggest that it become part of the required curriculum for an ACS Chemistry major. For a person going into research, learning how to process information from scientific journals is a necessity and something that isn’t really done in any other chemistry class. Peer discussion on research was also emphasized, which is unlike other courses, yet essential to most jobs in the field. This course has, in short, most strongly conveyed the link from my undergraduate studies to skill application in the field than any other course I’ve taken. I recommend it to any and all science majors. It’s fantastic.

The Chemical Roots that Drive Obesity
It shouldn’t come as a surprise to hear that obesity is one of the most prevalent medical concerns in the United States. In fact, 30%  of the US population has obesity and 30% of these individuals also has diabetes. Our society is a point where the number of cases of type 1 diabetes in young people under the age of 18 is increasing. In order to combat this rise in obesity and diabetes regulations have been placed on fast food businesses, requirements such as food nutrition labels have been implemented, and grassroots campaigns against chemicals such as Red Dye and High Fructose Corn Syrup have sprung up around the country. These regulations have been put in place as an attempt to curb people’s eating habits and make them aware of just what they are eating. However, the issue of obesity and diabetes may not stem solely from society’s increased consumption of food. In order to understand the cause of these issues we must delve into the brain and observe the interactions of two chemicals: Leptin and Insulin.
of the US population has obesity and 30% of these individuals also has diabetes. Our society is a point where the number of cases of type 1 diabetes in young people under the age of 18 is increasing. In order to combat this rise in obesity and diabetes regulations have been placed on fast food businesses, requirements such as food nutrition labels have been implemented, and grassroots campaigns against chemicals such as Red Dye and High Fructose Corn Syrup have sprung up around the country. These regulations have been put in place as an attempt to curb people’s eating habits and make them aware of just what they are eating. However, the issue of obesity and diabetes may not stem solely from society’s increased consumption of food. In order to understand the cause of these issues we must delve into the brain and observe the interactions of two chemicals: Leptin and Insulin.
While insulin is a term you’ve probably heard about, you may be unfamiliar with leptin. First, a brief summary of insulin. Insulin is a peptide hormone which regulates the amount of glucose taken in by cells throughout the body. Within the brain, insulin controls glucose intake by neurons, regulates acetylcholine, and contributes to memory function (http://www.hbo.com /alzheimers/science-insulin-in-the-brain.html). Similarly leptin is also a peptide hormone. Leptin is an important regulator of food intake (appetite) and body weight. In the brain leptin and insulin receptors are primarily found within the hypothalamus in a region known as the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Chemicals such as neuropeptide Y (NPY), agouti related protein (AgRP), and proopiomelanocortin (POMC), which are released based on leptin and insulin concentrations, cause the neurons in this region to be known as appetite-regulating neurons. When concentrations of insulin and leptin are high, POMC is released which reduces food intake and when concentration are low, NPY and AgRP stimulate food intake.
/alzheimers/science-insulin-in-the-brain.html). Similarly leptin is also a peptide hormone. Leptin is an important regulator of food intake (appetite) and body weight. In the brain leptin and insulin receptors are primarily found within the hypothalamus in a region known as the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Chemicals such as neuropeptide Y (NPY), agouti related protein (AgRP), and proopiomelanocortin (POMC), which are released based on leptin and insulin concentrations, cause the neurons in this region to be known as appetite-regulating neurons. When concentrations of insulin and leptin are high, POMC is released which reduces food intake and when concentration are low, NPY and AgRP stimulate food intake.
 It might be helpful to know some of the Biochemistry of leptin signaling. Leptin stimulates cytokine receptors, which activate the JAK/STAT pathway towards gene expression. JAK, janus kinase, is a protein bound to the cytokine receptor, which upon stimulation of the receptor becomes phosphorylated. The phosphorylated JAK then creates a bind site for STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) molecules. STAT then enters the cell nucleus where it transcribes DNA for gene expression.
It might be helpful to know some of the Biochemistry of leptin signaling. Leptin stimulates cytokine receptors, which activate the JAK/STAT pathway towards gene expression. JAK, janus kinase, is a protein bound to the cytokine receptor, which upon stimulation of the receptor becomes phosphorylated. The phosphorylated JAK then creates a bind site for STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) molecules. STAT then enters the cell nucleus where it transcribes DNA for gene expression.
Now that some of the Biochemistry is out of the way, it is important to discuss how levels of leptin contribute to the rising levels of obesity in the US population. People with obesity have a flood of leptin in their system so the cytokine receptors become resistant to the overabundant leptin. This means that the appetite controlling chemical POMC is not produced because the neurons are not receiving leptin. Therefore, the signal stop food intake in never activated. On the other side of the metabolic disorder spectrum, people with anorexia have high levels of leptin without receptor resistance, thereby expressing POMC and preventing craving for food intake. Therefore, dyregulation and imbalance in leptin levels in the brain can cause various metabolic disorders such as obesity.
A Reflection on the Semester
It’s hard to believe that it’s over. I’m not going to lie, I was nervous about this class knowing that it was going to be a good deal of biology, despite the neurochemistry name. Proteins, receptors, lipids, synapses…. As we say up here in Minnesota, ‘Ufda!’ I feel that I’ve grown in a lot of ways over the past semester.
The idea of a paper a week was very intimidating at first, but a 15 page scientific article no longer fills me with dread and foreboding (the last five pages are usually references anyway!) and my knowledge about the brain and how it works has definitely increased, although there wasn’t a lot there before, at least not a very in depth knowledge. I really appreciated coming together on Monday to a safe place and accumulate the things in the article that we did not understand. It made me feel less alone in the strenuous process of trying to get a basic idea of what the paper was talking about and gives a great method for getting deeper knowledge out of any paper that you read. Wednesday, or information day, when we all come together to give synopsis of the extra information dug up on subjects we didn’t fully understand always went quickly, but it was nice that if there was something that I missed it was on the wiki to be reexamined at a later time.
I think that Fridays were out “BREW” days (BREW is Concordia College’s motto ‘Becoming Responsibly Engaged in the World’). It was interesting to see everyone’s perspective on the subject as a health issue and how it relates to social issues, not just the pure science of it. More than that, it allowed us to reflect on science and its impact on society as a whole and moral dilemmas that occur within the scientific community.
On the whole, I have taken some new skills and improved other skills through this capstone experience. I have become better at reading and deciphering information from scientific papers as well as presenting that information in a relatable manner, both through the Wednesday information sharing sessions and through the blog posts. They say that being able to teach information is the best way to cement it in your own mind, and I cannot agree more. I think that this experience with scientific papers will help my own writing, better knowing what is expected in published papers. All in all, this class has been a good experience for me and I really appreciate the change in pace from so many other science classes that I have taken in the past.