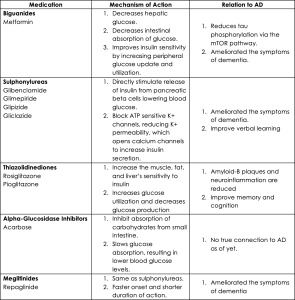
Introduction
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease classified by cognitive impairments of memory loss, critical thinking, and social skills. Recently, research has begun connecting the lack of insulin to the progression of Alzheimer’s. Insulin is connected to improved cognitive function and memory. However, decreased insulin has previously been observed as being a defect of the pancreas and playing a role in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
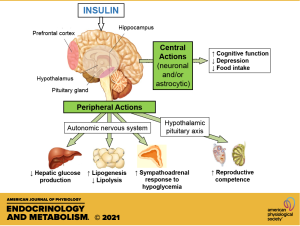
Insulin in the brain
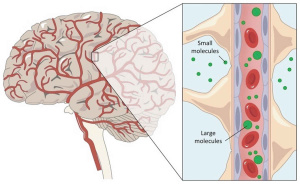
Insulin enters the brain either peripheral or is produced directly in the brain. Insulin produced peripherally must cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) through a transport system to act within the brain. Once in the brain insulin binds to insulin receptors (IR) which are primarily located within the hippocampus and the cortex. The binding of insulin to IRs results in the regulation of metabolism, cell differentiation, survival, and growth. However, in the presence of insulin resistance Alzheimer’s Disease begins progressing.
Insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s
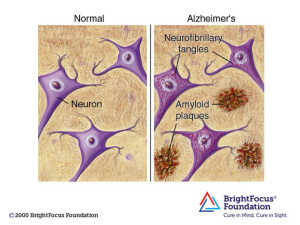
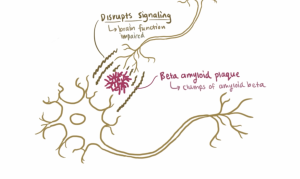
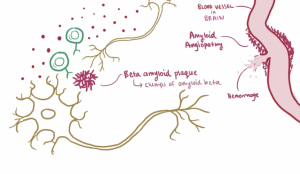
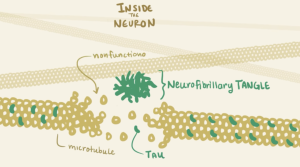
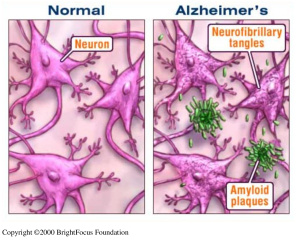
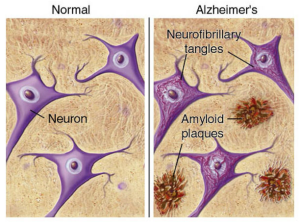
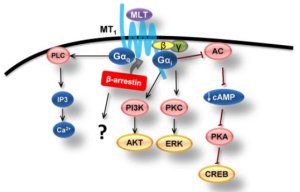
The amyloid beta protein is naturally produced within the brain and is responsible for assisting in nerve growth and repair. However, improper cleaving by the secretase enzyme results in a misfolded beta sheet secondary structure protein that binds to other misfolded proteins. The oligomer that forms from the misfolded protein binding is an amyloid beta plaque. Amyloid beta plaques bind to IRs therefore, competing with insulin to bind to the IR. Increased binding of plaques result in the formation of more plaques and lessen the presence of insulin and the amount of insulin binding to IRs in the brain. Additionally, the binding of amyloid-beta plaques to the insulin receptors causes signaling dysfunction of the PI3K pathway which in turn activates the GSK-3ß pathway. The dephosphorylation of GSK-3ß pathway leads to the phosphorylation of Tau proteins. Tau proteins make up the microtubules found in neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). The formation of NFTs block synaptic communication and eventually lead to neuronal death. The presence of plaques, NFTs, and neuronal death are the major characteristics of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Conclusion
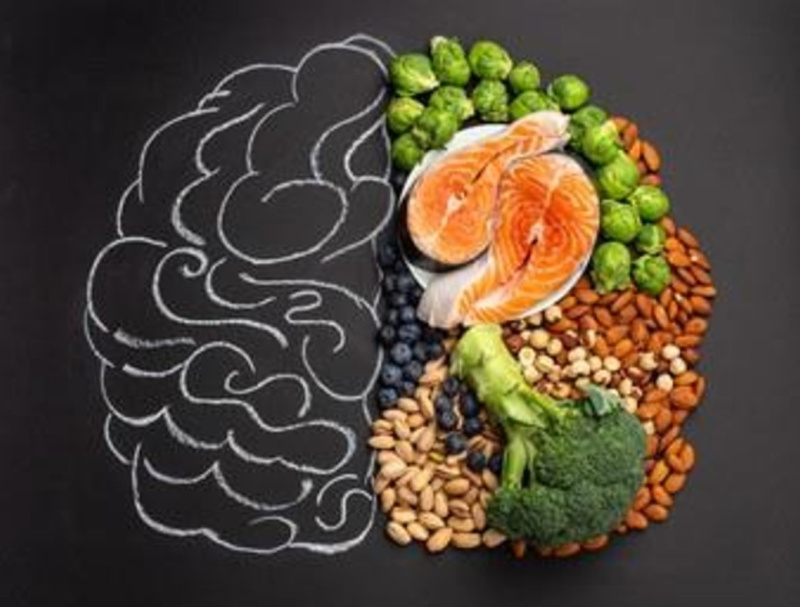
A major risk factor of amyloid beta plaque formation is based off of diet. A diet consisting of high omega-3 fats, reduced sugar, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while avoiding processed foods are shown to reduce the potential of amyloid beta plaque formation and buildup. However, if Alzheimer’s has already set in neuronal death cannot be reversed but it could be slowed or stopped. No definite treatments exist to stop the spread of AD, but promising results have been observed with exenatide-4 treatment. Exenatide-4 targets and activates the PI3K and Akt pathways which phosphorylates and deactivates the GSK-3ß pathway. Deactivation of the GSK-3ß pathway will decrease tau phosphorylation, directly limiting NFT formation and slowing neuronal death and the affects of Alzheimer’s.
Exenatide-4 structure