Marijuana or cannabis. Some say it is bad, others say its good. Lets dive down deep to discover the ins and outs of the endocannabinoid system.
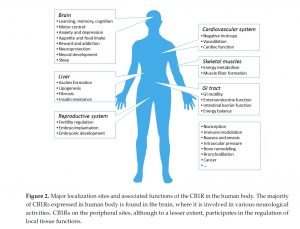
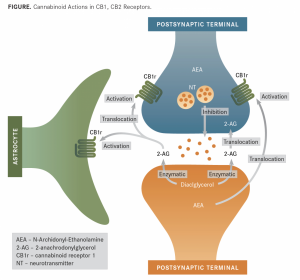
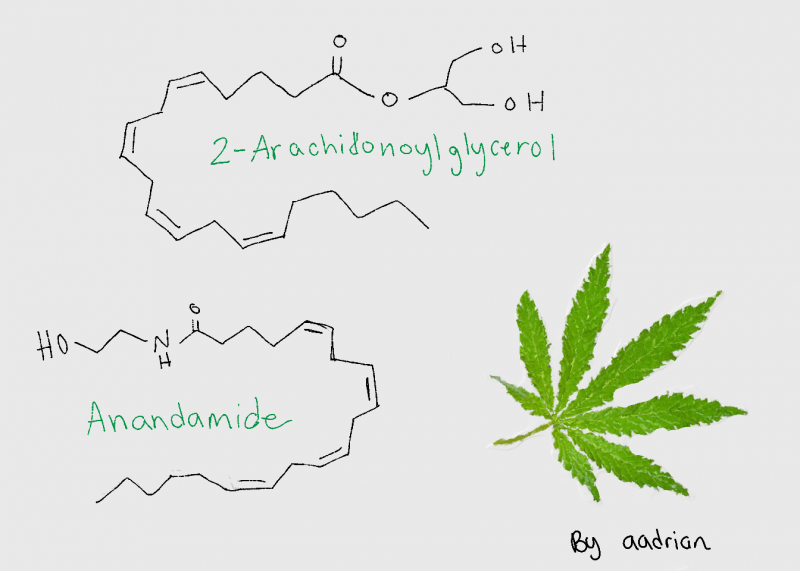
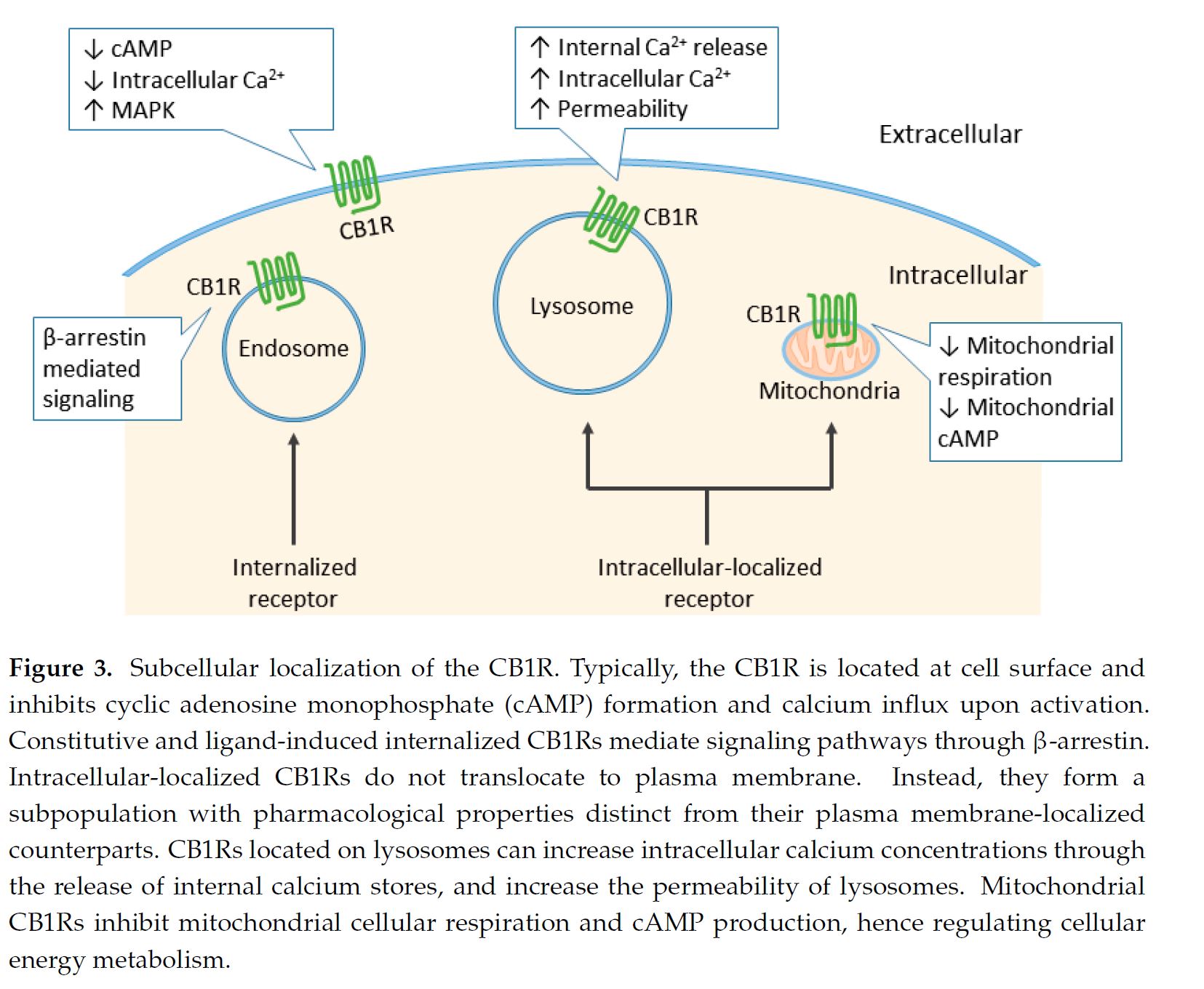
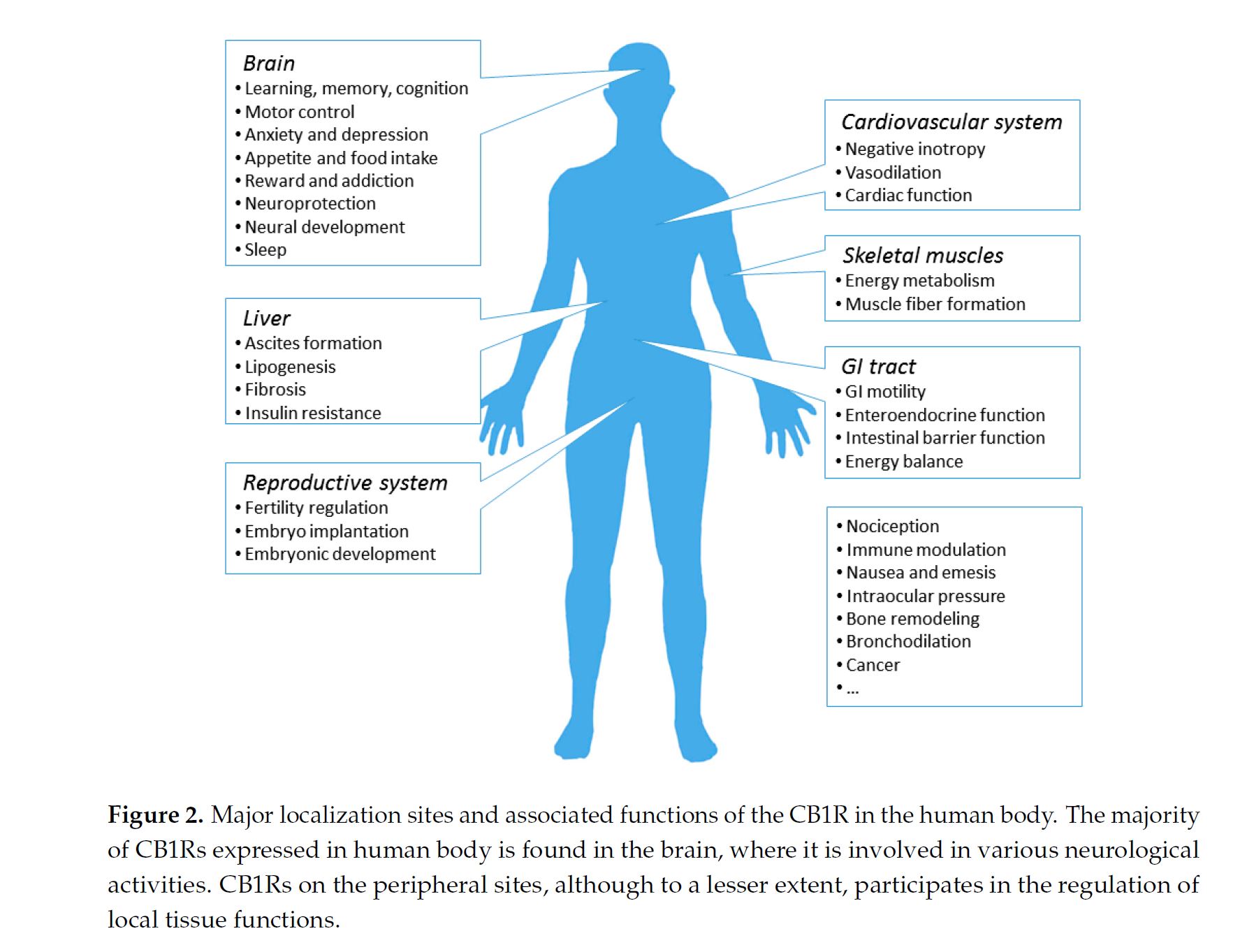
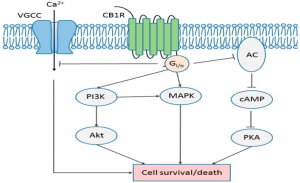
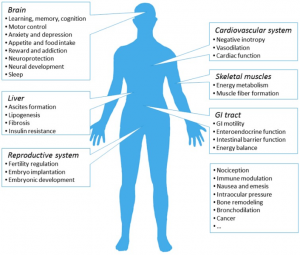
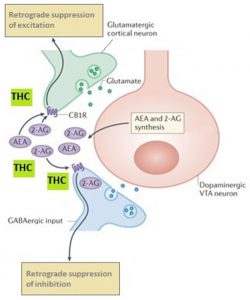
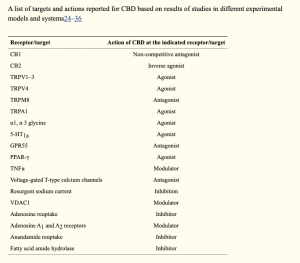
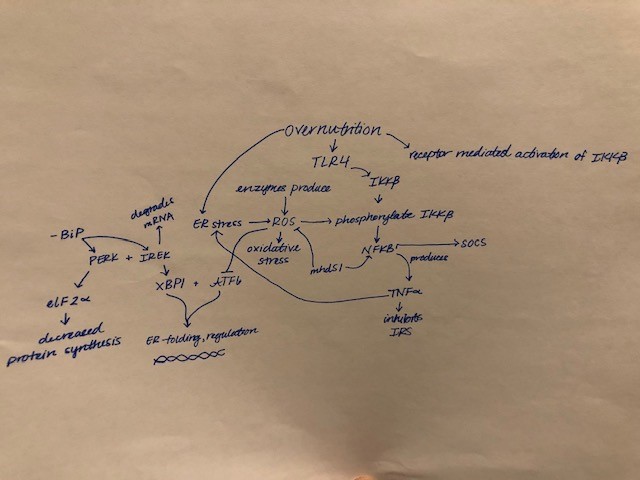
Cannabis is a plant that is grown and yields CBD and THC. THC activates cannabinoid receptors and leads to the common high due to the psychoactive component. More is still being learned about CBD, and it is known that it is use as a treatment option for pain. THC uses two different receptors to bind, CB1R and CB2R. CB1R is dominant in brain and skeletal muscle whereas CB1Rb has higher expression within the liver and pancreatic cells due to its involvement in metabolism. CB2R are found in the testes and lower levels in brain reward regions. Endogenous agonist (AEA) and 2-AG are important endocannabinoids that bind to both receptors. AEA has a high-affinity and partial agonist of CB1R and inactive to CB2R. 2-AG is a full agonist aga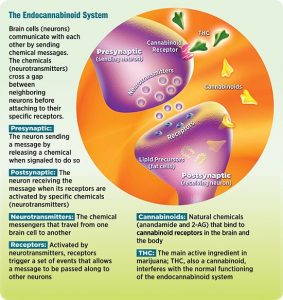 inst both receptors, but has a low affinity. CB1R can inhibit GABA and glutamate release from presynaptic terminals meaning it can modulate neurotransmission. This is important because CB1R plays a neuroprotective role against excitotoxicity, inhibits nitric oxide, and increases brain derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF). So how is this all beneficial or hurtful to the body?
inst both receptors, but has a low affinity. CB1R can inhibit GABA and glutamate release from presynaptic terminals meaning it can modulate neurotransmission. This is important because CB1R plays a neuroprotective role against excitotoxicity, inhibits nitric oxide, and increases brain derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF). So how is this all beneficial or hurtful to the body?
CB1R has been observed in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. In Parkinson’s, there is an upregulation of CB1R and the endocannabinoid system. In Huntington’s, there is a progressive loss of CB1Rs and worsens over time. Currently, CB1R is being looked at as a way to control appetite. The most common use of cannabinoids however is for pain. In cancer patients who are undergoing chemotherapy or radiation, they typically experience a loss of appetite. Cannabinoids are being used to help increase their appetite to maintain a healthy weight to continue treatment and increase their well being. Along with stimulating appetite, it also reduces nausea, vomiting, and alleviates pain. As mentioned above, one property of endocannabinoids is the neuroprotective effects against excitotoxicity. This is commonly associated with seizures due to the over active firing. Endocannabinoids can reduce this, resulting in dramatic decreases for those that have epilepsy. In fact, some families who have young children with severe epilepsy will move to a state that has legalized medical marijuana. In moving to these places, these families have had children or family members go from hundreds of small seizures and frequent gran mal seizures to less than a quarter of that. This shows that the endocannabinoid system can drastically reduce neurological diseases and their symptoms to increase the way of life of these people. However, there are some fears that are associated with endocannabinoids such as the addictive or gate way drug tendencies. However, cannabis does not actually have an addictive chemical like nicotine. Cannabis is considered a gateway drug but not a lot of research has been done, in fact, alcohol a frequently consumed item is considered a gateway drug.
The endocannabinoid is a complex system that is still being studied for pros and cons. A lot of the research that is now available is leaning towards more benefits than harms, especially for neurodegenerative diseases in which this system can help improve the quality of life.