
Alzheimer’s disease:
New research keeps shedding light on Alzheimer’s Disease prevention and treatment. New studies have linked Diabetes Mellitus Type II, which is a major disease in the United States, as a major factor that can contribute to someone developing Alzheimer’s Disease in the future. Insulin functioning in Alzheimer’s Disease is a major topic that is being explored. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S019701862030098X?via%3Dihub
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone that is released by the body after food is eaten to lower blood sugar. Insulin helps to lower blood sugar by activating cells to store sugar in a long chain, called glycogen, which can be used as a fuel reserve as a gas tank is a fuel reserve for a car.
Variations in diet, even genetics, can change how much insulin needs to be produced by the body. Diets high in sugar and saturated fats, think of fats that are solid at room temperature like coconut oil, can increase insulin production. Eating diets that are high in sugar and saturated fats for many, many years, can increase the likelihood of developing insulin resistance as seen in Figure 1.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance essentially means that the cells of the body are no longer being activated to the same capacity because the cells have gotten used to so much insulin. Think of this as putting a phone on energy saving mode compared to never putting the phone on energy saving mode, the phone screen is not as bright, the screen turns black faster when not being used, and does not function as usual.
Developing insulin resistance can be increased from having an excess amount of body fat, which can result in obesity. Severe insulin resistance can be diagnosed as Diabetes Mellitus Type II. https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/insulin-resistance
Insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease
Developing Type II Diabetes reduces the effectiveness of insulin in the body and brain. Insulin is mainly produced by the pancreas. The pancreas is not the only organ to produce insulin, neurons within the brain produce also insulin. Insulin is essential for neuronal function, especially memory and cognition.
Reducing the effectiveness of insulin within the body can contribute to some of the physical hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease in conjunction with memory loss and decreased cognition. In one review article, insulin resistance from Type II Diabetes Mellitus completely disrupts normal neuronal functioning. Typically, insulin and insulin growth factors stimulate insulin receptors, which activates IRS, recruiting PI3K, which activates Akt. Akt will deactivate GSK3b, and Akt will go on to activate transcription factors, such as mTor. mTor will activate genes in the neuron to produce more insulin receptors, as well as helps the neurons to grow and survive, as seen in Figure 2.
When insulin receptors are no longer stimulated to the same capacity by insulin and insulin growth factors due to insulin resistance, IRS, PI3K, and Akt activation is decreased or completely stopped, which will allow GSK3b to become overactive. This protein can decrease a neuron’s capacity for growth and life by producing factors within the neuron that stimulate death, as well as neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) and amyloid beta (Ab) plaques, seen in Figure 2. NFT and Ab plaques are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease. These buildups are toxic to neurons and cause neuronal death, which is why symptoms of impaired cognition and memory loss are common in Alzheimer’s Disease.
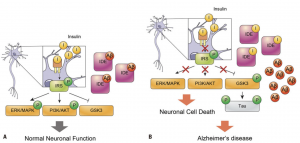 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6255119/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6255119/
NFT and Ab plaques can be regulated by insulin. Insulin can help to clear Ab plaques and helps to stop NFT formation, which is why insulin resistance is being looked at for potential therapies to treat Alzheimer’s Disease. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6255119/
Now what?
Alzheimer’s Disease does not have a cure, but exciting research is being done on drugs that target the insulin pathway to slow and potentially stop the progression of Alzheimer’s. One major factor that can be controlled is diet and exercise. By reducing the amount of saturated fat and sugar in the diet can decrease the likelihood of developing insulin resistance later on in life. Exercise can decrease precursors of saturated fat in the blood and muscles, which promote insulin resistance. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2019.00577/full
Why care about Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s Disease not only takes a toll on people who are diagnosed with this disease, but also their families. More and more people are becoming diagnosed with this, especially in the United States, and more preventative care and treatment options need to be developed.