Everybody has a family member with alzheimers or knows somebody that does. It seems like that rates of this neurodegenerative disorder are going up, but is this really the case? Are the rates of alzheimers going up because of the environments or because of our diets, or simply because the life expectancy is going up as well and this disorder is sprouting up because people are living longer now. This is a disorder that effects many people close to home, and there are a lot of people out there that grow up knowing they are at a high risk for alzheimers because it runs in there family. So what is this disorder? What is going on in the brain?

One of the most common things we know about this disorder is that people begin to lose their memories. Both long term and short term memory are affected in the early stages and slowly progress to get worse as the disorder takes its course. The first form of memory that is truly affected is episodic memory. This is what helps you remember little things like where you put your school backpack, or that you have your oven on and are cooking food in there. In alzheimers, this is seen early on as people forgetting where they put their car keys, or why they walked into a room. This is so commonly overlooked in those beginning stages because people will believe that they are just getting older and have normal memory lapses. Because of this, alzheimers can go unnoticed for quite some time, which can be dangerous for the individual, especially if they live alone.

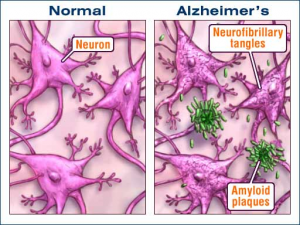
In the alzheimers brain, there are things called amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These are very prominent, and when you look at the brain of an alzheimers person, they are one of the reasons why you see so many spaces and gaps. Those gaps are also there because neurons are dying and disappearing essentially. The neurofibrillary tangles are created through a process. The PI3k pathway in the brain becomes overactive, which causes the tau protein to become hyperphosphorylated. This hyperphosphorylation leads to the development of the NFT’s (neurofibrillary tangles). These tangles are connected to cognitive decline and behavioral changes. There is still much to be studied with alzheimers, and treatments are being tested. It will be interesting to see where the science is at 20 years from now, and if we have found a cure or not. Even if we haven’t found a cure, have we found a way to treat or slow down the effects of the disorder.
Sources:
https://moodle.cord.edu/pluginfile.php/625272/mod_resource/content/0/AD%20and%20insulin%20signaling.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2655107/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3898682/
Im Losing My Keys, My Time, and My Mind…
Imagine waking up in the morning and seeing the snow hit the ground. But…. Isn’t it July? I remember having plans with uncle Tom to go fishing this afternoon… Whats going on?

This is a bit of an extreme example of what an Alzheimer’s patient may think about when dementia sets in, however, it is a very real aspect that most Alzheimer’s patients go through. What is even tougher to understand is the complexity of this disease and all the factors that play a role in developing Alzheimer’s. From genetics to environmental exposures, Alzheimer’s disease is incredibly scary.
When looking closely at Alzheimer’s, there are a lot of biological cues that can lead to diagnosis. Accumulation of tau proteins (neurofibrillary tangles) and amyloid-beta plaques (AB-42) is found in a majority of cases, followed with neurodegeneration of the entire brain. Essentially, this accumulation of AB-42 was thought to be an over production of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), but recent studies have shown that the production of APP is still normal, and it is in fact the removal of AB-42 in the body that has slowed down. How AB-42 is made in the first place is a simple enzymatic error occurring during enzyme cleaving (normal cleaving gives AB-40).

Why this error is occurring in some individuals more than others is due to a gene mutation of PSEN-1, PSEN-2, or APPG. These genes encode the formation of the APP protein, and when a mutation occurs, the APP protein is synthesized incorrectly. This allows improper cleaving to occur more often, and AB-42 plaques to build up faster, and more recently. However, not all of Alzheimer’s disease is caused genetically.
In a majority of Alzheimer’s patients, it is found that a upregulated signaling of the mTOR pathway of neurons is causing a systematic overload within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to occur, thus leading to cell atrophy (neurodegeneration). Essentially, the ligand that upregulates this pathway, is the combination of TNF-alpha and insulin. Alzheimer brains are found to be more insulin resistant, which may result in no counteraction against TNF binding, assuming that insulin binding effects the binding affinity or ability of anterograde signaling for TNF. When this over abundance of TNF binding is occurring, protein synthesis in the ER is sent into overdrive. This induces an inflammatory response within the neuron, which will likely cause cell death.

Because of insulin’s involvement in the brain and this particular instance, diet and exercise play a key role in staving off Alzheimer’s and possibly even preventing it. Future research is also looking into the importance of being type-2 Diabetic and how that can play as a risk factor in the disease too. At this point in time, there is just too much involved with Alzheimer’s disease that some make the argument “it’s just aging”. Although this statement is some what true, with a majority of diagnosed individuals being over the age of 65, I myself would still like to believe that we should all be able to grow old and die someday, without losing our mind both physically and psychologically.
Key Things You Need to Know About Alzheimer’s Disease
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a disorder of the brain that affects a person’s memory, thinking and overtime the ability to enact in simplest tasks.
- It is most prevalent with age, older individuals tend to have it more and It is the most common cause of dementia in older adults.
- The majority of people with Alzheimer’s are 65 and older, this does not mean the disease is not seen in the younger population.
- Over 200,000 people under the age of 65 have younger-onset Alzheimer’s disease
- Alzheimer’s is also the 6th leading cause of death in American and 3rd among the older population just behind heart attacks and cancer.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
- The most common symptom is difficulty remembering newly learned tasks/ information.
- Disorientation
- Mood and behavior changes
- Deepening confusion about events, time and place
- Unfounded suspicions about family, friends and professional caregivers
- Difficulty speaking, swallowing and walking.
Family members need to know those symptoms and take them seriously if they are presented in their loved ones.
Alzheimer’s and the brain
Before we go any farther let us understand what happens in the brain of a person with Alzheimer’s. They are two things you need to know, Plaques and Tangles.
- Plaques are deposits of a protein fragment called beta-amyloid that build up in the spaces between nerve cells.
- Tangles are twisted fibers of another protein called tau that build up inside cells.
Abnormality in these structures have been found in individuals with Alzheimer’s. Another key player is the loss in connectivity between neurons and the brain. As we age those connections tends to weaken hence leading to memory loss. Other studies have linked Alzheimer’s to over activation of the PI3-k (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)/ AKT pathway which is initiated by insulin. The video below does a better explanation of how the brain is affect in Alzheimer’s (please watch).
How Long Can a Person Live with Alzheimer’s disease?
- If you are over 80 life expectance with the disease is about 3 to 4 years, and 10 years for younger patients.
Is there a cure?
The answer is no, there is no cure. Although current Alzheimer’s treatments cannot stop Alzheimer’s from progressing, they can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms and improve quality of life for those with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers. Today, there is a worldwide effort under way to find better ways to treat the disease, delay its onset, and prevent it from developing.
Clink the link below to see how you can help a loved one with Alzheimer’s
https://www.alz.org/national/documents/care_10waystohelpafamily.pdf
If you or a loved one is looking for help call the numbers below or visit the websites for more information.
1-800-272-3900 (toll-free, 24/7)
1-866-403-3073 (TTY/toll-free)
info@alz.org
www.alz.org
Early Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most dreaded neurological disorders. Characterized by severe memory loss and cognitive declined, Alzheimer’s is relatively easy to distinguish from other disorders in its later stages, but it is more difficult to detect early on. Given the lack of effective treatment options for late stage Alzheimer’s disease, it’s crucial to diagnose AD before symptoms become severe.
Although the ultimate cause of Alzheimer’s is unknown, several neurological abnormalities are associated with the onset of the disease. Beta-amyloid plaques, formed by the accumulation of improperly folded amyloid proteins, disrupt synaptic connectivity and neural plasticity (1). Accumulation of these plaques is correlated with the over-activation of a signaling pathway known as the P13-kinase/Akt pathway, which is regulated by insulin and insulin-like growth factors (1).

Inflammation is also thought to play a role in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease by disrupting the structural integrity of synapses between neurons (1).
Another protein, called “Tau,” is responsible for holding other proteins, called microtubules, together outside of the cell. These microtubules help connect neurons to each other (2). In individuals with Alzheimer’s, Tau is dissociated from these microtubules and forms tangles within neurons, and it no longer holds the microtubules together, resulting with disruptions in neuronal connectivity (2).

These abnormalities are often present long before symptoms become severe enough to cause some individuals to seek a diagnosis, and the accumulation of Beta-amyloid plaques and Tau tangles are practically irreversible. Therefore it’s important to detect Alzheimer’s early on in order to slow the progression of the disease and to maintain the best quality of life possible. Here are early signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease that elderly individuals and their family members should be mindful of:
- Short-term memory problems, like forgetting recently made appointments.
- Lapses or mistakes in long-term memory, such as forgetting important dates (like birthdays or anniversaries), or forgetting the names of familiar people.
- Difficulties with keeping track of information, such as bills.
- Difficulties with concentration and attention.
- Getting confused with time or places. An example would be forgetting which season it currently is.
- Visual problems, such as problems with depth perception or the inability to determine color.
- Problems with speech and writing, like stopping in the middle of a sentence or calling objects by the wrong name.
- Changes in mood.
- Decrease in the ability to make sound judgments, such as falling for scams that would usually be easy to identify as malicious.
- Social withdrawal.
This list was compiled from information given by the Alzheimer’s Association, and can be accessed by the following link: https://www.alz.org/10-signs-symptoms-alzheimers-dementia.asp
While Alzheimer’s is difficult to treat at any stage, treatments are much more effective early on, before symptoms become severe. Unfortunately it is often difficult to distinguish some of the early symptoms from the normal cognitive changes that occur with age, which means it’s imperative for elderly individuals to seek advice from medical professionals if more than one of these symptoms become apparent.
Sources
1.https://moodle.cord.edu/pluginfile.php/625272/mod_resource/content/0/AD%20and%20insulin%20signaling.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3385935/
- https://www.alz.org/10-signs-symptoms-alzheimers-dementia.asp
Image Credits
1. https://www.everydayhealth.com/news/10-essential-facts-about-alzheimers-disease/
2. http://www.namrata.co/case-study-alzheimer-disease/amyloid-plaques-and-neuro-fibrillary-tangles/
3. https://alzheimersnewstoday.com/2014/11/03/tau-protein-leads-to-neuronal-death-in-alzheimers/
The Complexity of the Brain – Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a debilitating sickness and becoming more prominent in our society. We see it on our TV shows (Grey’s Anatomy lovers), we experience it through friends or family members suffering, and we hear about it in all those intense and uplifting research commercials. However, besides memory loss and confusion, what exactly do we know about Alzheimer’s disease and how is it affecting the brain?
What is Going on in the Brain of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the overactivation of a biological pathway in the brain initiated by insulin. Insulin binds receptors in the brain which go through a series of chemical changes to become activated. This leads to the further activation of PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway. Normal function of this pathway is important to the brain; however, it should be activated in moderation. These three proteins are inside the cells that make up our brain, neurons, and regulate normal cellular function and growth. However, when this overactivation occurs, the mTOR protein hyper-phosphorylates (chemical change) Tau and APP proteins in the brain. Once Tau is activated, there is an accumulation of proteins in the brain known as neurofibrillary tangles. Once APP is activated, beta amyloid plaques build up in a similar manner.
Overall, ventricle size increases due to the decrease in brain matter from overaccumulation of proteins. Too many proteins cause brain dysfunction so unnecessary proteins are not being broken down and the cells of the brain, neurons, begin to die.
When it comes to memory loss, the hippocampus shrinks due to brain cell death. The hippocampus is a very important brain structure involved in memory so atrophy to this region is what causes the symptoms associated with memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease.
The Importance of Knowing the Biology of Alzheimer’s Disease
The overview of the biology of Alzheimer’s disease does not even scratch the surface of its true complexity. Therefore, treatment options are limited and are being researched tirelessly. However, knowing more about some of the biology can at least push research forward in the right direction so people can live there best lives up until death.
The next, time you watch your favorite TV show with Alzheimer’s diseases prevalent or you see a commercial on researching the disease, you can hopefully be informed of the intensity this disease is on the brain and the importance of finding a cure.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S053155651300065X
How Your Present Can Impact Your Future in Alzheimer’s Disease
Would you ever think that the McDonald’s trip you took earlier today could lead to the development of Alzheimer’s in your future? Well, there are signs that it actually could. I had never thought about over nutrition as a cause of this debilitating disease that impacts the lives of so many, but there is more to do with it than just genetics.
Activation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway:
This pathway in our body, is normally activated by insulin. When the pathway is activated, its job is to promote normal aging and transcription in the body. However, it is seen in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) that this pathway is over activated. Normally, activation of the pathway causes the activation of IRS which then activates PI3-K. PI3-K is a kinase that is responsible for phosphorylating PIP2. The new PIP3 is then able to activate a protein AKT which then can phosphorylate other molecules like GSK3B, FOXO and MTOR. In regular function, GSK3B is inhibited which allows the proliferation of the B-catenin pathway an changes transcription factors in the cell. FOXO is also inhibited and is involved in a normal stress response. MTOR is activated at the end of the pathway because it causes the inhibition of the pathway as a negative feedback. When over nutrition is involved, the body is unable to handle the breaking down the sheer amount of proteins involved and creates faulty proteins called ABeta. These faulty proteins can also activate the PI3-K pathway. This overall leads to insulin resistance, because as the pathway is over activated it leads to an abundance of MTOR which shuts down the pathway all together. Therefore, more insulin is needed in order to cause the same response in the body. Eventually, the body continues to make faulty proteins and continues with insulin resistance until the body elicits neuron/cell apoptosis which leads to a decrease in transmission of signals in the brain.
Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease:
Although there a drug remedies involved with AD, there is no definite cure for AD, the medications can only slow the onset of the disease. One form of these medications is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which basically allows our excitatory neurotransmitter acetylcholine persist in the brain so that signals are more likely to occur. Another medication option is known as memantine which acts to decrease the amounts of glutamate in the brain. This helps slow the progression of AD by decreasing the amounts of Calcium in the brain. Another promising drug in clinical trials currently is called CNP520 which works to decrease the amount of ABeta production and therefore decreases the activation of the PI3-K pathway that then decreases insulin resistance.
Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention:
Although some forms of AD are highly genetics related, most forms have a high environmental component. What we eat and how we treat our body throughout our lives can have such an impact on the development of diseases in our future. Over nutrition is a huge problem in our society which can lead to many other problems besides things like obesity and type 2 diabetes and AD might be one of those problems.
For more information about how the PI3-K pathway is involved in AD read:
PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. which can be found at: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S053155651300065X
Cover Photo from:
https://www.alzheimers.net/resources/what-is-alzheimers-disease/
Going, Going, Gone – A Prominent Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a disease that is infamous to many. The devastating effect it can have one an individual and those around them along with the high prevalence rate has lead to this disease being a hot topic for research.
In an article by O’ Neill, the PI3K and mTOR pathway was examined as likely culprits, if at the very lease accomplices in this nasty brain disease. The article explains that the PI3K pathway is activated by insulin which then leads to an increase in mTOR, which is a receptor or rapamycin. This increase then leads to a protein called Tau becoming phosphorylated.
Phosphorus in the body acts as a switch either turning on or off a protein. In the case of Tau, phosphorylation acts an activator of this protein, and with these new modifications this protein becomes a dangerous one. Phosphorylated Tau leads to neurofibulary tangles (NFT), which act as road blocks in the brain. With synapses having a harder time connecting with one another, neurons start to weaken and eventually die.
As bleak as this pathway may seem, the uncovering of PI3K in the role of AD does have promising implications. Studies have been shown that exercise can help lower the amount of phosphorylated Tau, which means less NFTs which cause the cognitive decline in individuals.
Currently in the US, there is a study that is in the recruiting stages that’s goal is to uncover which kinds of exercise can help support memory. Ultimately, they are looking for exercises that can be given to individuals to help treat and prevent AD . Although the role an over-activated PI3K/ mTOR pathway can have detrimental effects, the discovery of this pathway in AD can help us understand what causes this form of dementia and hopefully what can treat it.
For more reading on the PI3K pathway check out:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23470275
For more reading on the current US trial with exercise and AD check out:
https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/putting-exercise-test-people-risk-alzheimers
Feature Image:
https://cbd-international.net/effects-cannabis-oil-alzheimers-disease/
Alzheimer’s Disease: The Most Prominent Form of Dementia
Forms of Dementia
The dictionary definition of dementia is stated as a chronic or persistent disorder of the mental processes caused by brain disease or injury and marked by memory disorders, personality changes, and impaired reasoning. Although there are cases of early onset dementia, the senior population is most highly affected by these diseases. We can contribute much of the development of the disease to old age; the pathways in our brains can repair themselves to an extent, but wear and tear eventually take their toll of much of our senior population. There are many forms of dementia, with these five forms being the most commonly known:
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
- Presents with short-term memory deficits
- Atypical presentation includes behavioral or language deficits
- Hallmarks are amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, synaptic and neuronal loss with subsequent brain atrophy
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)
- Presents as fluctuations in cognition with pronounced variation in attention and alertness
- Motor features of Parkinsonism
- Progresses rapidly
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD)
- Slow progression
- Early loss of personal and social awareness, signs of disinhibition
- Mental rigidity and inflexibility, hyperorality, stereotyped and preservative behavior
- Symptoms include depression and anxiety, somatic preoccupation, emotional unconcern
- Reduction and stereotypy of speech, echolalia
- Display loss of movement, rigidity, and tremors
Pick’s Disease (PD)
- Affects frontal cortex
- Usually manifests between 50-60 years of age
- Distinguished from FTD by presence of characteristic intraneuronal argentophilic Pick inclusion bodies found at autopsy
- Present with prominent personality changes and impaired executive function
Vascular Dementia (VaD)
- Temporal association of cognitive deficits with stroke and evidence of cerebrovascular disease
Alzheimer’s Disease
How Important Is the Environment in Autism Development?
Autism Risk Factors
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which problems with communication, interest, social ability, and behavior are exhibited. There are many environmental risk factors that contribute to the development of autism and/or genetic risk factors. It has not been determined if there is a certain percentage that environmental risk factors contribute to autism compared with genetic risk factors, but it is commonly agreed that the major risk factors for autism are genetic. One important piece of information to note is that there is no scientific evidence to support the idea that vaccines cause autism, and this hypothesis has been disproven time and time again.
These environmental risk factors are grouped into two different categories: zinc deficiency and immune system abnormalities. Many of these risk factors are able to be grouped into both categories as well, and zinc deficiency can also lead into immune system abnormalities, so it is a complicated web of risk factors.
A big picture disruption in the body that can lead to autism is glutamate. Many of these risk factors will lead to glutamate excitotoxicity, which then has a multitude of effects throughout the brain and body.
Zinc Deficiency Environmental Risk Factors
- Copper overload
- Malnutrition/Atypical eating behaviors
- Gastrointestinal Tract abnormalities
- Low melatonin levels
- Maternal diabetes
Immune System Abnormalities
- Toxins
- Psychiatric drugs leading to prenatal stress
- Perinatal stress
- Increased parental age
- Pronatal viral infection
- Zinc deficiency
- Melatonin deficiency
Is A Cure Possible?

After learning about the long list of not only genetic, but also environmental risk factors associated with autism, it seems as though a cure is far off, if not impossible. This is not true though; researchers are optimistic about being able to make a more specific hypothesis attributing the cause of autism to a specific event or pathway.
How Did We Get to Holland? a Journey to Autism
Sesame Street writer Emily Perl Kingsley is often asked to describe what it is like to raise child with disability. She describes it as planning a trip to Italy, but unexpectedly arriving in Holland. Her entire poem is moving, but she explains that while the trip was unexpected, there are still many things to enjoy about Holland.
The concept of Holland is transferrable to any parent of a child with a disability, but in this blog, we are going to dig into the Holland of Autism.
What is it like to go to Holland?

For individuals who experience autism, they can land anywhere in the spectrum where they may be met by challenges in social skills, verbal and nonverbal communication, repetitive behavior, and sometimes intellectual disabilities.
There are many guides along the way to help individuals with autism. Depending on their needs, these range from peer social interactions in the classroom to family development at home. Technology has also had an important role in reaching individuals with autism, as they may find it easier to communicate through apps on phones and tablets.
Why does Holland exist?
Autism is a neurological disorder that is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. While autism-related genes are the greatest contributor, recent research has taken interest in the environmental factors that may further activate these genes.
Of the many environmental factors Andreas Grabrucker proposed to have an influence on autism incidence, they could be connected into two broad categories: immune system disruptions and zinc deficiency.
Some immune system disruptions were traced back to prenatal/perinatal stress, exposure to toxins, or increased parental age. The zinc deficiency could stem from malnutrition, copper overload, or a melatonin deficiency. Interestingly, the zinc deficiency could also contribute to immune system abnormalities.
Why is zinc so important?
The presence of zinc is incredibly important to the normal function of glutamate neurons. Autism is characterized by glutamate excitotoxicity, which means that too much glutamate is being released and causes the neuron to be overactive.
Zinc normally decreases glutamate release, so when that is not present, glutamate is continually released. Zinc is also important for proper function of other receptors and the structural integrity of the neurons. If there is plenty of zinc, they are able to stack certain proteins to make the synapse of the neuron stronger.
If Holland isn’t so bad, why are we trying to fix it?

All in all, engaging a child with a disability like autism is truly a journey. Some parents may say that they would not trade this journey for anything, as the diagnosis is part of their child’s identity. However, if they were given the choice to provide their child an autism-free life, I struggle to understand how any parent would deny that of their children.
We should continue to advocate for those affected by autism. Not only to provide those individuals with the services necessary to adapt to everyday life, but to also support research in finding a cure for autism.
While a prenatal zinc tablet may not be the answer, this recent research may lead to a zinc-based treatment in the future to diminish the environmental factors on autism.
“